Table of Contents
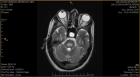
Acute ischemic stroke management in a patient with ventricular assist device
Published on: 23rd December, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8872699685
Ventricular assist device is a portable machine which is also called an artificial heart for the patients who have terminal heart failure. The device maintains the heart’s vital functions until the suitable donor is found for the heart transplantatio... n. It can be applied to either ventricles or both (biventricular). Although the device provides independence for the patient, it also has life-threatening complications. Such as infection, stroke secondary to thromboembolism, hemorrhage depending on anticoagulant use, right heart failure… and most of the time it is really hard to manage those complications. We will present a case, who had ischemic stroke as a complication of VAD even though he has been using aspirin, warfarin and had effective INR value. Show more >
Ivabradine versus carvedilol in the management of palpitation with sinus tachycardia among recovered COVID-19 patients
Published on: 23rd December, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8872655874
Introduction: One of the major complications among COVID-19 patients include cardiac arrhythmias. Commonest arrhythmia is sinus tachycardia which is usually associated with palpitation causing discomfort to patients. In this study, we present a compa... rative study of use of Ivabradine vs. Carvedilol for sinus tachycardia in post-COVID-19 infected patients.
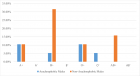
Method: 50 consecutive recovered COVID-19 patients with sinus tachycardia were included in this open labelled RCT. 25 patients received Ivabradine and remaining 25 received Carvedilol. Single therapy non-responders were treated with Ivabradine with Atorvastatin.
Results: The mean age of all patients is 48.8±7.66 years (Males 49.5 ± 7.21 years; Females 47.68 ± 8.23 years). The mean heart rate (MHR) of all patients is 125.52 ± 9.07/min (Males 125.67 ± 8.78/min; Females 125.26 ± 9.5/min). After five days of single drug therapy the mean drop in the heart rate was 35.04 ± 10.55/min (Males 34.41 ± 9.71/min; Females 36.05 ± 11.72/min), resulting in 27.88 ± 8.11% (Males 27.38 ± 7.56%; Females 28.69 ± 8.89%) reduction in MHR. Among the two groups, the Carvedilol group showed improvement of MHR in 14(56%) patients; whereas in Ivabradine group 18(72%) patients improved out of 25 patients each (p: 0.2385). In the Carvedilol group the MHR reduced from 128.6 ± 8.44 to 95.68 ± 10.63 (p < 0.001), which is statistically significant; similarly, the Ivabradine group showed a MHR from 122.44 ± 8.62 to 85.28 ± 10.52 (p < 0.001). The monotherapy therapy non-responders were treated with dual-therapy of (Ivabradine + Atorvastatin).
Discussion: Ivabradine is more effective in controlling heart rate compared to Carvedilol. Also, Ivabradine group scores very well in ‘patient-satisfaction’ with regards to symptom (palpitation) relief.
Conclusion: The COVID-19 sequelae of sinus tachycardia can be better controlled with Ivabradine when compared to Carvedilol. Show more >
Post-extrasystolic potentiation differentiates “true” from “pseudo” Low-flow, Low-gradient aortic stenosis
Published on: 16th December, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8872657684
Post-extrasystolic potentiation (PESP) is a marker of contractile reserve and refers to the augmentation of left ventricular contractility due to preload recruitment and rise in intracellular calcium following a premature beat. In this case report we... show that PESP might be a safe and helpful aid to evaluate low flow, low gradient aortic stenosis and contractile reserve in the cathlab, thereby reducing the potential risk of complications associated with intravenous dobutamine evaluation and reducing unnecessary testing. Show more >
Antibiotic induced changes to mitochondria result in potential contributions to carcinogenesis, heart pathologies, other medical conditions and ecosystem risks
Published on: 2nd October, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8689024240
With the discovery by Calghatgi (2013) that three common antibiotics (Abs) increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen (ROS) and lipid peroxide (LP) and depleted their natural absorbant glutathione led me to investigate further the potential impacts of t... hese genotoxic substances on carcinogenesis. The range of impacts on mitochondria and cellular DNA varied by antibiotic to those consistent with known prior contributions to carcinogenesis. Specific cancers probably increased by these changes were HCC, RCC (KCC), CRC, cancer of the esophagus. Tumor suppressor gene mutations resulting from LP were noteworthy in this regard and mutations induced in CRC were consistent with those found in carcinogenesis of CRC. In addition depression of short chain fatty acids in microbiomes were found which depress the immune system increasing risk of all cancers. Many cancers were increased according to epidemiological studies linking Abs with elevated odds ratios, with one concern in particular, fatal breast cancer. The impact of loss of functionality of the mitochondria was also linked to depression of the citric acid cycle and therefore ATP which deflected metabolism to glycolysis, the Warburg mechanism also increasing risk of all cancers, favoured by cancer cells. In conclusion, some portion of many cancer types are probably increased in likelihood by number, type and frequency of Abs treatment and chronic residue exposure which varies from individual to individual. This led me to propose a three pronged carcinogenesis mechanism for Abs. 1. Cancer critical mutations 2. Immune depression 3. loss of mitochondrial functionality leading to Warburg effects. Damage to mitochondria were also noted by common pesticides tested in China and cancer associations were also found for many pesticides supporting a similar contributory etiology. Heart health concerns were raised by these findings because of the myriad mitochondria in the heart and because of long term reliability needs. Studies suggesting hearts were affected by Abs and pesticide exposure were presented. Because of their geographical ubiquitousness and the huge range of diseases associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, antibiotics and pesticides and bacteriocidal biocides are of concern for biodiversity and life in general. I propose research steps to evaluate Abs safety and suggest directions for further research and make suggestions on ways to ameliorate Abs toxicity. Show more >
Clinical profile and surgical outcomes of children presenting with teratology of Fallot
Published on: 14th September, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8667862731
Background: Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a very common cyanotic congenital heart disease presenting early at birth with various degrees of cyanosis. If left uncorrected surgically, can lead to death.
Objectives: This study is aimed at determining pat... tern and surgical outcome of children with teratology of Fallot in a budding health facility in India over a year period.
Result: A total of 51 children were diagnosed of TOF over the period, of which 66.7% were males with mean age of 48.14 ± 45.36 months.
The surgical outcome showed only 3.9% mortality. The death was among children >1 to 5 years. The mean number of days in intensive care unit (ICU) was 5.8 ± 11.2 days. 82.4% of the patients were off-pump post-operatively, compared to 17.6% with re-pump. Among those who had re-pump, 77.8% were males and among those without re-pump, 64.3% were likewise males (χ2 = 0.6, p = 0.41). About 92.2% (47/51) of patients had pulmonary regurgitation post-op, ranging from mild to moderate regurgitation. 51.1% of the regurgitations were mild while 25.5% and 23.4% were moderate and severe regurgitations respectively.
Post-operative VSD was detected in 51% (26/51) of the patients. The post-op right ventricular pressure (RVOT) was significantly lower than that of pre-op pressure, 10.8 ± 1.5 mmHg vs. 31.7 ± 4.5 mmHg (pair t test = 8.7, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Timely surgical repair is crucial in alleviating several morbidity and mortality associated with teratology of fallot. Pulmonary regurgitation is a very common sequel after surgery and can result in death. Show more >

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."