Review Article
Endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptors (ESBAR) and its analogs (review)

Victor Tsirkin1*, Alexander Nozdrachev2, Elena Sizova3, Tatyana Polezhaeva4, Svetlana Khlybova5, Marina Morozova6, Andrew Trukhin1 Julia Korotaeva7 and Grigory Khodyrev1
1Department of Biology and Methods of Teaching Biology, Vyatka State University 610000, Kirov, Russia and *Institute of Neuroscience of Kazan State Medical University, 420012, Kazan, Russia
2Department of General Physiology, Saint-Pererburg State University, 199034, Saint-Pererburg, Russia
3Department of Food Products Expertise, Kirov State Medical University, 610027, Kirov, Russia
4laboratory of Cryophysiology of Blood, Institute of Physiology of Komi Scientific Center, Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, 167982, Syktyvkar, Russia
5Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Kirov State Medical University, 610027, Kirov, Russia
6Department of Biomedical Disciplines of Vyatka State University 610000, Kirov, Russia
7Department of Biology, Kirov State Medical University, 610027, Kirov, Russia
*Address for Correspondence: Victor Tsirkin, Department of Normal Physiology, Kazan State Medical University, Russia, Email: tsirkin@list.ru
Dates:Submitted: 16 October 2018; Approved: 27 October 2018; Published: 29 October 2018
How to cite this article:Tsirkin V, Nozdachev A, Sizova E, Polezhaeva T, Khlybova S, Morozova M, Truhin A, Korotaeva Yu, Khodyrev G. Endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptors (ESBAR) and its analogs (review). J Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2018; 3: 064-078. DOI: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001028
Copyright License: © 2018 Tsirkin V, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Keywords: Catecholamines; beta-adrenergic receptors; Endogenous modulators of adrenergic receptors; Smooth muscle; Myocardium, erythrocytes; Platelets; Pregnancy; Labor; beta-adrenoceptor inhibitory mechanism
Abbreviations: AR: Adrenoceptors; beta: ARIM: beta-adrenoceptor inhibitory mechanism; CA: Contractile Activity (of strips); CAU: Contractile Activity of the Uterus; LPC: Lysophosphatidylcholine; LS NPRUH: Longitudinal Strips of Nonpregnant Rat Uterine Horn
Abstract
The results of the 20 years studies of the presence in blood serum and other body fluids of endogenous modulators of adrenergic and M-cholinergic impact as a component of humoral link of autonomic nervous system. The article is devoted to the endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptor (ESBAR) - water-soluble low molecular weight substances, analogs of which are histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, mildronat and preductal. It is shown, that separate dilutions of human serum and animal (as a source of ESBAR) and analogs of ESBAR ways to enhance the effectiveness of activation of beta-adrenoceptors (AR) of smooth muscle (uterus, coronary and renal arteries, trachea, stomach), myocardium, erythrocytes and platelets (respectively influenced of histidine and tryptophan). It is reported that content of ESBAR in human serum (according to the titers of its dilution) depends on the sex and the presence of somatic diseases, and at women are also on the stage of reproduction and obstetric complications It is discussed possible mechanisms of ESBAR action, its physiological role, including as a component of beta-adrenoceptor inhibitory mechanism for myometrium, as well as the prospect of the use of analogs of ESBAR, including for the prevention of preterm labor, and for the treatment of bronchial asthma, coronary heart disease, hypertension and heart failure.
Introduction
Studying chemoreactivity of isolated myometrium of pregnant women and animals (rat, rabbit, pig), we have identified [1-5], that there are a variety of uterostimulatory, i.e. substances, which increase of contractile activity of the uterus (CAU), e.g., oxytocin, serotonin, histamine, but there is only one substance that able to inhibit spontaneous activity and /or induced (by uterostimulators) activity. It is likely, adrenaline, which interacts with beta2-adrenoceptors (AR) of myometrium. Given the available by the time the data is relatively high effectiveness of beta2-agonistin at pregnant women with threat of premature labor (TPL) [6], we have proposed a hypothesis about the functioning the so-called beta-adrenoceptor inhibitory mechanism (beta-ARIM) at pregnant women, the degree of influence on the CAU reduced only before labor [7-9]. According to this hypothesis, at pregnancy in uterine myocytes increased expression of beta2-AR gene that leads to the dominance of the beta2-AR above alpha- AR. Therefore catecholamine of blood serum and amniotic fluid, activating the beta2-AR of uterine muscle cells, inhibit the spontaneous CAU and induced CAU, for example, by oxytocin, 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) and histamine (with appropriate receptors). But contrary to this hypothesis, a circumstance known by that time well enough - a phenomenon of desensitization, i.e., loss of effectiveness of the activation of membrane receptors during continuous exposure to the agonist. It was demonstrated in our experiments with isolated myometrium of human and animals, including in relation to the interaction catecholamines with beta2-AR [10]. But in that time the mechanism of desensitization does not have any detailed information about the process of phosphorylation of receptors associated with G-protein as the basis of desensitization and the existence of enzymes, it is now considered to be involved in this process, including kinases of alpha-AR or beta -AR [11], protein kinase A [12], and protein kinase C [13]. However, we have assumed that the effective functioning of the beta-ARIM addition to beta2-AR agonist and it is necessary factor preventing desensitization of these receptors and thereby constantly maintain the effectiveness of their activation [7-9]. We hypothesized that this factor is contained in the blood of mother and possibly in the blood of the fetus. In this regard, we conducted an experiment with the longitudinal strips of nonpregnant rat uterine horn (LS NPRUH), in which assessed the efficacy of the effect of adrenaline on the CA of the strips three times - 1) initially, 2) against exposure to blood serum of pregnant women and 3) after its removal (Figure 1). It was assumed that the presence in the serum of the desired factor in certain dilutions of blood serum should rapidly and reversibly raise the efficiency of inhibition of spontaneous CA of these strips under the influence of adrenaline. Should take two fundamentally important in terms of methodological explanations. 1) LS NPRUH unlike the circular strips of of nonpregnant rat uterine horn mainly reflect the activity of the longitudinal layer of the myometrium, which is characterized by high expression of beta2-AR, in connection with which the adrenalin even in very low concentrations inhibits of spontaneous CA of these strips; but in the circular layer of the uterus of nonpregnant rats no dominance beta2-AR, in this connection, the adrenaline does not inhibit spontaneous CA of these strips, even in very high concentrations [14]. Therefore, to detect the presence of serum hypothetical modulator of beta2-AR best suits LS NPRUH. 2) The threshold concentration of adrenaline, which causes the inhibition of spontaneous CA of LS NPRUH depends on the phase of the estrous cycle (maximum - in metaestrus) [4,14], and also depends on the season and other climatic factors [15]. Therefore, for the detection of the blood factors, that increases the effectiveness of beta2-AR activation in experiments with LS NPRUH. Initially need to find the concentration of adrenaline, which is close to the threshold or slightly above it. All these factors taken into account when searching factor, which enhance the effectiveness of beta2-AR activation. The result of this research was a series of your publications in 1997 year [16-18], which reported that the serum of pregnant women in a dilution of 1:100, 1:500 or even 1: 103 is able to increase the degree of inhibition of spontaneous CA of LS NPRUH under the influence of a threshold concentration of adrenaline. Those (Figure 1), in the presence of blood serum of adrenaline in the concentration close to the threshold, he showed himself as adrenaline in a concentration close to the maximum [16-18]. In these articles, the first time a hypothetical factor that increases the effectiveness of the beta2-AR activation, was named endogenous sensitizer of beta-AR, or ESBAR. They have also been reported [16-18], that the content of ESBAR, according to the blood serum dilution rate in which there is ESBAR- activity, depends on gender – men have content of ESBAR lower than that women, and women depends on the presence of pregnancy – at pregnancy content of ESBAR increases, which probably contributes to the formation of beta-ARIM. It was noted [16-18], that ESBAR was found in urine, saliva, in the cerebrospinal fluid, and at pregnant women - in the amniotic fluid. This meant that ESBAR can pass through various barriers - to the brain, kidneys, salivary glands, to the fetus, and from it - in the amniotic fluid. Thus, it has been proved the existence factor that enhances the efficiency of the beta2-AR activation, i.e. ESBAR.
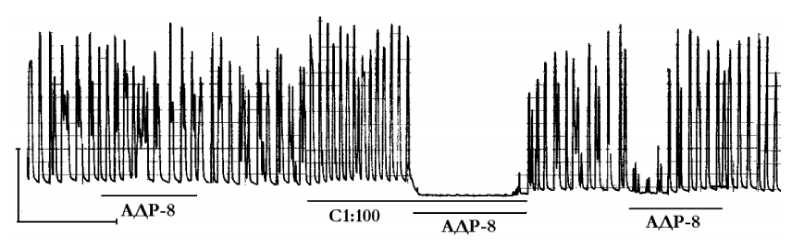
Figure 1: Mechanogram of longitudinal strips of nonpregnant uterine horn rats showing β- adrenosensitizing effect of 100-fold dilution of venous blood serum (C1: 100) of the pregnant woman. The horizontal lines under the mechanogram represent the time exposure of the serum (С:100) and adrenaline (8×10–8 g/ml; AДР-8). Calibration — 10 mN, 10 min. From [10]. Адр-8 — adrenalin, 10–8 g /Мl; С1:100 — serum of venous blood in dilution 1:100.
These publications preceded yet another of our paper [19], which was first reported that a 100-fold dilution of serum of umbilical cord blood of newborns improves beta- adrenoreactivity circular segments of the pig coronary arteries. If the initially adrenaline, even in very high concentration (10-6 g/ mL) did not reduce their tone, increased high potassium solution (25 mM KCl) Krebs, then the action of adrenaline along with 100-fold dilution of serums causes a very marked decrease in tone (Figure 2). This allowed to conclude that serum indeed contains ESBAR which can improve efficiency of beta2-AR activating not only myocyte of uterus but myocytes of coronary artery. We believed that these works [16-19] are of interest to ESBAR. However, it took almost 20 years, during which time there and our other articles on ESBAR, but so far we have not seen a single work of other laboratories, which would confirm or refute our findings. Perhaps this is due to the fact that to date nature ESBAR is not defined, it is not isolated in pure form and is not set location (s) of its synthesis.
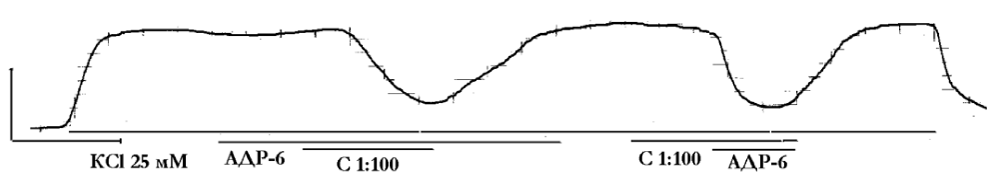
Figure 2: Mechanogram of circular strip of porcine coronary artery showing β- adrenosensibilizatotory activity of 100-fold dilution of umbilical cord blood serum (С 1:100) on the background of tone, induced by hyperpotassium (25 мМ KCl) Krebs solution. The horizontal lines under the mechanogram represent the time of exposure to substances, including hyperpotassium Krebs solution (25 mM KCl), adrenaline (10 -6 – g/ml, ADR-6) and the blood serum (С1:100). Calibration — 10 mN, 10 min From [9]. 25 мМ KCl — hyperpotassium (25 мМ KCl) Krebs.
During these years, efforts have been made to clarify the physiological role of ESBAR, in particular, the ability of ESBAR to improve the efficiency of activation of beta2-AR of smooth muscle from pig coronary artery [20,21], the arteries and veins of human umbilical cord [22-24], cow renal artery [25-28], cow trachea [21,29-31], rat stomach [32,33], and also myocardium of frog [34-37], rats [36-42] and humans [43-45] and human erythrocytes [46]. In addition, our efforts were made to find analogs of ESBAR [21,27-29, 35-37,39-43,45-60], to study the mechanism of action of ESBAR and its analogs [36,38-43,56-61], on the role of ESBAR in the pathogenesis of somatic diseases - coronary heart disease [62-64], arterial hypertension [25 26,65,66], bronchial asthma [30,31], and gastric acid-related diseases [33], as well as a number of obstetric complications as the weakness of labor activity, threat of premature labor, preeclampsia and placental insufficiency [15,67]. Preliminary analysis of these dates has been made in our two books [15,68].
Nature of ESBAR, analogs of ESBAR and sources of ESBAR production
We have attempted to study the nature of ESBAR. But to get pure ESBAR, determine its structure and molecular weight failed, including the lack of expensive equipment. At the same time determined that ESBAR-activity of blood serum a is relatively stable to 60 minutes of boiling and also for long-term storage, including up to 24 hours at 37°C, or up to 14 days at 4°C or 90 days at -20°C. It is also obvious, that ESBAR is the water-soluble substation as all blood serum dilutions, including exhibiting ESBAR- activity, preparing with Krebs solution [15,18,68]. Preconcluded that ESBAR is a low molecular weight substances, as an ultrafiltrate of blood serum of pregnant women, as well as its low molecular fraction wich obtained by gel filtration on Sephadex G10, retain ESBAR- activity in experiments with LS NPRUH [15,68]. In view of these data it has been searched substances capable exhibits ESBAR-activity. It was found [68-70], that among of the 37 different substances (of low molecular weight with a different physiological effect) including 20 amino acids, 30 substances did not have ESBAR- activity. Among them -antihipocsants (meksidol and emoksipin), acids of Krebs cycle and its salts (α-ketoglutaric acid, oxaloacetic acid, fumarate, succinate sodium), nicotinic acid, blocker Na+-K+-pump (strophanthin K), hormones (thyroxine, hydrocortisone), protein synthesis blocker (adrioblastin), a substance similar in structure to trimetazidine (piperazine) or histidine (imidazole), and 17 amino acids (β-alanine, L-arginine, L-asparagine, L-aspartic acid, L- glutamine, D,L-glutamic acid, L-lysine, L-leucine, L-cysteine, D, L-glycine, D,L-valine, D,L-isoleucine, D,L-methionine, D,L-proline, D,L-serine, D,L-threonine, D, L-phenylalanine. At the same time it was established [15,47,55,56,58,68,70], that ESBAR-activity exhibited 3 amino acids - L-histidine (3х10-8-10-5 g / mL), L-tryptophan (10 -5 g/mL) and D, L-tyrosine (2х10-6- 10-5 g / mL), as well as used in cardiology metabolic drugs - trimetazidine (preductal) and trimethylhydrasine propionate (mildronat) [48-50,52,53,56,58] (Figures 3,4). Furthermore, ESBAR-activity showed nitroglycerin (10-5 g/mL) and ethanol in high concentrations (9,6 х 10-3 g/mL) [68,69]. Data on the ability of the histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, mildronat and preductal improve efficiency activate of beta2-AR were obtained in experiments with the LS NPRUH, including background spontaneous CA and under tone caused by high potassium (60 mM KCl) Krebs solution (Figure 3) and against the background of an artificial reduction of the efficiency of the activation of beta2-AR by ozonated (5х10-8 g/mL) Krebs solution [51-53], lysophosphatidylcholine [71] or non-selective beta-blocker propranolol [56,58,59]. When this has been shown relative selectivity analogs ESBAR - in experiments with LS NPRUH they did not exhibit this effect against acetylcholine response [72]. Given that the histidine, tryptophan, and tyrosine are natural components of blood serum, it was suggested that ESBAR is at least one of these three amino acids. Taking into account the concepts of beta-ARIM, the degree of influence on the myometrium which should increase during pregnancy [7-9], as well as our data about increasing of ESBAR-activity of blood serum at pregnancy [16-18], was studied blood levels of 20 amino acids, including histidine, tryptophan and tyrosine at pregnant women and parturient. These studies, however, have not confirmed our hypothesis [54,67]. Contrary to expectation levels of these three amino acids are not increased at pregnancy. Therefore, we hypothesized that ESBAR- activity of blood serum is determined not only by the content of the three amino acids, but also the presence in it other any substances [54,67].
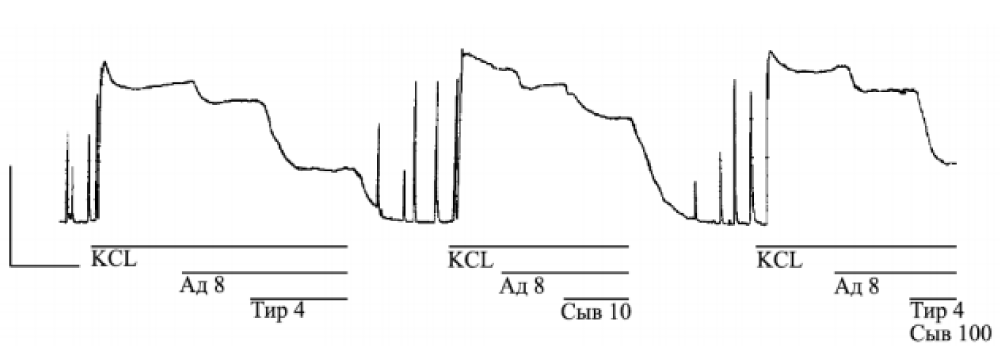
Figure 3: Mechanogram of longitudinal strip of nonpregnant rat uterine horn showing of β- adrenosensitizing effect of tyrosine, 10–4 g/ mL (tyrosine 4), 100-fold dilution of serum (serum 100), including at their combined effect on KCl-induced contracture. Horizontal lines indicate the time of exposure to substances, including adrenaline (10–8 g / ml; Ад 8. Calibration — 10 mN, 10 min. From [20]. KCl - hyperpotassium (25 мМ KCl) Krebs solution; Ад 8 — аdrenaline, 10–8 g/mL Тир 4 — tyrosine,10–4 g / mL; Сыв 100 — serum of venous blood in dilution 1:100.
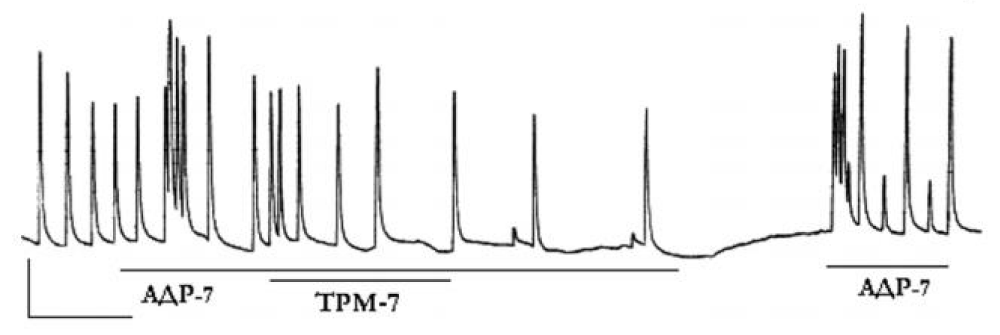
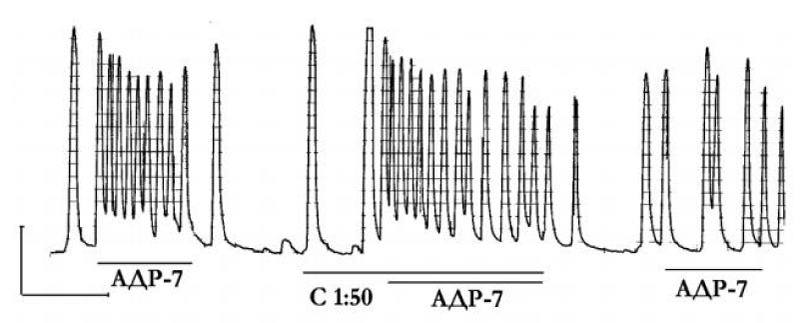
Figure 4: Mechanogram of myometrium strip of pregnant woman showing β- adrenosensitizing effect of trimetazidine. Horizontal lines under the mechanogram reflect the time of exposure to substances, including trimetazidine, 10–7 g / ml (TPM-7) and adrenaline, 10–7 g/ mL (АДР-7). Calibration — 10 mN, 10 min. From [38]. АДР-7 — adrenaline, 10–7 g/mL TPM-7 — trimetazidine, 10–7 g / ml.
Adrenergic synapses of the myometrium as a source of ESBAR
Given the fact that among the amino acids having ESBAR-activity was tyrosine, known as a precursor of the catecholamines, we hypothesized, that the adrenergic nerve fibers of myometrium can to be source of ESBAR. To prove this hypothesis a series of experiments held [15,18]. In this experiments part of the longitudinal strips of uterine horn of nonpregnant and pregnant rats, as well as strips of myometrium of nonpregnant or pregnant women served as a prospective source of ESBAR («donors» of ESBAR) and identification of ESBAR- activity of perfusate flowing from the strip – «donors», carried out on a test object, in which quality in all series used LS NPRUH. At the same time, the ability of the perfusate flowing from the «donor» strip, modify the test object response to adrenaline, which was used at concentrations close to the threshold (10-9, 10-8 or 10-7 g /mL). In experiments in which strips- donors were strips of nonpregnant uterine horn of rats, it was found that the perfusate collected from donor strip after the beginning of perfusion prior to onset of spontaneous CA (about 20 minutes) had ESBAR-activity, i.e. enhanced the inhibitory effect of adrenaline (10-9, 10-8 or 10-7 g /mL) in 38.6% of experiments. Against the background of spontaneous CA of strips-«donor» ESBAR- activity of perfusates was observed in 46.2% of experiments. Against the background of the 20-minute transmural electrical stimulation of the strips- «donor», which was held in a 30-second bursts of electrostimulation (inside – 3 impuls /s,duration - 0,5ms, voltage - 50V), going every 30 seconds, ie, just 10-11 packs, ESBAR -activity was noted in 33.3% of experiments, and after transmural electrostimulation - in 46.2% of experiments (respectively, P1-,P2-, P3- and P4-perfusates collected for 20 minutes each). If the "donor" is the longitudinal strips of uterine horn of pregnant rats, the values were, respectively, 21.4%, 42.8%, 57.3% and 36.4%. In similar experiments, in which «donors» were strips of myometrium nonpregnant women (obtained at hysterectomy about uterine fibroids), these values were, respectively, 42.9%, 28.6%, 0% and 14.3%, and in experiments in which the strips–«donor» were strips of myometrium of pregnant women (they are dissected with a planned caesarean section from the lower uterine segment) - respectively, 30.0%, 10.5%, 50.0% and 36.8% of experiments. These data allow us to conclude that: 1) the myometrium of rat and human can produce ESBAR; 2) in rats, when in strips generate of spontaneous CA it was increases of productions of ESBAR, and women (non-pregnant and pregnant women), by contrast, is reduced; 3) with transmural electrical products ESBAR at nonpregnant rats and (especially) at nonpregnant women is reduced, and in pregnant rats and pregnant women, on the contrary, increases. It is suggested that during pregnancy the so-called physiological sympathectomy of the uterus, which is described in the literature [73,74], is not a true denervation of the uterus, and it is the conversion of the mediator in the adrenergic terminals of the uterus - instead of noradrenaline, has a pronounced fluorescence, mediator becomes a precursor of catecholamines - tyrosine having a less pronounced fluorescence, which creates the illusion of sympathectomy. It is possible that this phenomenon is due to the suppression in the adrenergic synapses (under the influence of progesterone) of the expression of enzymes genes involved in the synthesis of dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA), dopamine and noradrenaline from tyrosine. Therefore neurotransmitter in the synapse becomes tyrosine, wich have high ESBAR- activity. Thus, tyrosine enhances the effectiveness of beta-AR activation on postsynaptic and extratsynaptic sites of the plasma membrane of muscle cells of the uterus under the influence of catecholamines of blood and amniotic fluid that prevents desensitization of these receptors. This provides braking CAU, ie implementation beta-ARIM. On the eve of the labor is likely to be gradual restoration of synthesis of classical adrenergic mediator - in the beginning it becomes dopamine and then noradrenaline. This reduces the degree of the effect of beta-ARIM on the myometrium and promotes the induction of labor, especially in this period and increased expression of alpha-AP gene.
Physiological properties and mechanisms of action of ESBAR and its analogs
The study of this issue mainly conducted experiments on LS NPRUH showing [61,68], that the blood serum of pregnant women and umbilical cord blood serum (as a source of ESBAR) and analogs of ESBAR –histidine and tyrosine, and in some cases tryptophan increase the inhibitory effect of above-threshold (but not maximum) concentrations of adrenaline, noradrenaline, and dopamine, but not enhance the inhibitory effects of synthetic beta2-agonists (ginipral and partusisten). This suggested that ESBAR and its analogs bind to the so-called amino acid site of beta2-AR and thus allosterically enhance its affinity to catecholamines, but not to synthetic agonists of adrenoceptor having different structure [61,68].
It has also been demonstrated [61,68], that the ability of ESBAR and its analogs (histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine) to improve the inhibitory effect of adrenaline is manifested not only on intact LS NPRUH having spontaneous CA, but also on LS NPRUH whose activity is enhanced artificially, e.g., high potassium depolarization (KCl 60 mM) Krebs solution (рис. 3) or oxytocin (5x10-3 IU/mL). It speaks of the universality action of ESBAR and its analogs, capable in any environment to improve the efficiency of beta2-AR activation In experiments with LS NPRUH was found [61,68], that the effect of ESBAR and its analogs observed relatively quickly - within the first 1-3 minutes from the start of exposure. After a 20-minute application of ESBAR its effect lasts 10 min (after exposure to 500- and 103-fold dilutions of serum) or 80 min (after exposure to 100-fold dilutions serum). ESBAR and its analogs exert their activity on the background of blockade of alpha-AR by nicergoline (10-6 g/mL) [68]. All this has allowed to argue [61,68], that ESBAR and its analogs are positive modulators of direct action, the effect of which is associated with increased affinity of receptor to agonist, to increase the efficiency of the transmission signal from the beta2-AR inside the cell effectors and to counter the development of desensitization. Indeed, in experiments with LS NPRUH it is shown that histidine (3 х10-8, 3х10-7 and 3х10-6 g/mL, but not 3х10-11 g/ mL) inhibits the development of desensitization observed during the 30-minute continuous exposure at high concentration of adrenaline (10-6 g/mL) [68,75], and histidine (10-6 g /mL) counteracts desensitization, developed at 5-fold the short-term (10 min) effects of adrenaline (10-7 g/mL) as an inhibitor of spontaneous contractions [58]. Accordingly, the histidine may have antidesenstization effect in different types of effects of adrenaline to the test object. We suggested [58,68,75], that the basis of histidine antidesenstization effect (histidine as analog of ESBAR) is its ability to inhibit enzymes that cause phosphorylation of the beta2-AR (kinase of beta2-AR or protein kinase A or protein kinase C) and / or activate of phosphatase and thereby reduce the degree of phosphorylation of the beta2-AR, which increases the efficiency of their activation. Unfortunately, we have not studied the effect of serum (as a source of ESBAR), histidine and other analogs of ESBAR on activity of enzymes involved are known [11-13] to desensitization and on phosphatase activity, which is known [76], prevents desensitization. However, regardless of the mechanism of histidine antidesenstization effect, we can talk about the possibility of using ESBAR and its analogs (tryptophan, tyrosine, mildronat, preductal) in clinical practice in order to improve the efficiency of activation of beta2-AR of cells [58]. In this aspect is important data on the interaction of blood serum (as a source of ESBAR) with analog of ESBAR [59]. They were obtained in experiments with LS NPRUH, which evaluated the effect of a unique ESBAR (histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, mildronat and preductal) on the inhibitory effect of adrenaline (10-8 g /mL), including the presence in the environment 100-fold dilution of serum of nonpregnant women study was conducted on the background tone, caused by high potassium (60 mM KCl) Krebs solution. (Figure 3). Thus the inhibitory effect was evaluated adrenaline source (1), its effect when combined action with one of the analogues of ESBAR at concentration of 10-4 g / mL (2), the effect of adrenaline together with 100-fold dilution of the serum of nonpregnant women (3) and the effect of adrenaline together with the 100-fold dilution of serum and with one of the analogues ESBAR (4). It was found that the 100-fold dilution of serum of nonpregnant women as a source ESBAR not prevent the expression of beta-adrenosensibilizatory activity of histidine and other analogues of ESBAR though potentiating effect analogues of ESBAR not observed. These data support our proposal about possibility of ESBAR analogs in clinical practice to increase the efficiency of activation of beta-AR of myometrium and other entities, for example, in the treatment of brachial asthma or for inhibiting preterm labor.
Ability of ESBAR and its analogs to restore the effectiveness of the activation of beta-AR, wich decline by the ozone, lysophosphatidylcholine or blocker of beta-AR
As part of the study of the mechanism of action of ESBAR and his counterparts in the experiments with LS NPRUH it was studied the role of these factors in the recovery efficiency of the activation of beta2-AR artificially reduced ozonated Krebs solution [51,53,77], or lysophosphatidylcholine [58,71], or blocker of beta-AR propranolol [56,58].
In particular, it has been established [51,53,77], that perfusion with ozonized Krebs solution (at a concentration of ozone in the environment 5х10-8 g /mL) reduces beta- adrenoreaсtivity of strips, i.e. reduces of the ability of adrenaline to inhibit their spontaneous CA or tonus induced by high potassium (60 mM KCl) Krebs solution. It was found that a 100-fold dilution of the serum of nonpregnant women as a source of ESBAR and L-histidine (3х10-6 g /mL), L-tryptophan (10-6 g /mL), D, L-tyrosine (2х10-6 g /mL), preductal (10-6 g/mL) and mildronat (10-5 g / mL), even on the background of the ozonized Krebs reduced adrenoreactivity of the strips to the initial level, i.e. remove beta-adrenoblocking effect of ozone. It is set for strips having spontaneous CA, and strips, which initially increased the tone of high potassium (60 mM KCl) Krebs solution. Moreover, in these experiments we have shown that a 100-fold dilution of serum and L-histidine (3х10-6 g/mL) even increased adrenoreaсtivity of myometrium i.e. increased the inhibitory effect of adrenaline (10-8 g/mL). Although the nature of beta-adrenoceptor blocking action of ozone is unclear, it can be assumed that the ozone is due to the accumulation of reactive species of oxygen destroys the native structure of proteins involved in signal transduction from the beta2-AR into the uterine muscle cells. Therefore, we identified the fact indicates the ability of ESBAR and its analogs (as original chaperones) to restore the native structure of proteins involved in signaling induced by activation of the beta2-AR.
We have also been shown [58,71], that beta-adrenoreactivity of LS NPRUH reduces by lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) - at a concentration 10-4 g / mL it reduces the ability of adrenaline (10-8 g /mL) to inhibit spontaneous CA of strips or lower tone of strips, wich induce by high potassium (60 mM KCl) Krebs solution. Thus histidine (10-4 g / mL) restores the effectiveness of beta2-AR activation. Similar results were obtained using a chicken egg yolk as a source of well-known [78] LPC. It been shown, that a chicken egg yolk in dilution 1:50 reduces beta- adrenoreactivity of LS NPRUH but histidine (10-5 g/mL) even in the presence of egg yolk restore it [58]. We explain the effect of beta-adrenoceptor blocking of LPC his ability as shown by several authors [78], to activate protein kinase C, which is known [13], together with the protein kinase A [12] and kinase of beta2-AR [11] phosphorylation of beta2-AR and thus speeds up the process of desensitization. From this perspective, it is believed, that the ability of histidine to restore the effectiveness of beta2-AR activation is probably due to his influence increased of beta2-AR dephosphorylation, which is likely to occur due to activation of phosphatase and inhibition of protein kinase C.
In another series of our experiments with LS NPRUH nonselective blocker of beta1- and beta2-AR propranolol (obzidan) at concentrations of 10-9 -10-6 g/mL dose-dependently partially or completely block the ability of adrenaline (10-7 g / mL) to lower the tone, increased with high potassium (60 mM KCl) Krebs solution [56,58]. Unlike propranolol selective beta1-AR blockers metoprolol and atenolol (10-9-10-6 g / mL) did not show this effect, indicating the absence of beta1-AR in myocytes of longitudinal layer of the uterine horn of nonpregnant rats [56,58]. On the background of propranolol 100-fold dilution of the serum of nonpregnant women (as a source of ESBAR) and any of its analogs - histidine, tryptophan and tyrosine (all -10-5 and 10-4 g / mL), and mildronat and preductal (both - 10-6 g / mL) restores the ability of adrenaline to show an inhibitory effect or hinder manifestation of the blocking action of propranolol. Thus, a series of control experiments indicated that partial blockade of inhibitory effect of adrenaline used in a concentration of 10-7 g / mL, propranolol should be applied at a concentration of 10-9 g / mL, and for full blockade - at a concentration of 10-7 g /mL. On a 100-fold dilution of the blood serum, these values for propranolol were respectively 10-8 g / mL (partial blockade) and 10-6 g /mL (complete block), i.e. in 10 times higher than in controls. On the background of histidine (10-5 and 10-4 g /mL), propranolol could partially or totally block the effect of adrenaline at a concentration of only 10-7 / mL, against tryptophan - at a concentration of 10-6 g/mL, against tyrosine - in concentrations 10-7 g / mL, against mildronat - in concentrations of 10-7 and 10-6 g / mL, respectively, against preductal - 10-9 and 10-6 g /mL. Thus, blood serum as the source of ESBAR and all analogues of ESBAR increased concentration of propranolol necessary for blockade inhibitory effect of adrenaline. Given that the propranolol is blocker of competitive type [79], i.e. it competes with catecholamines for binding site to the active site of beta-AR, the results suggest that ESBAR joining away from the center binding allosterically increases the affinity of agonist to the receptor and thus prevents the action of the blocker. A similar effect ESBAR and its analogs observed in experiments with rat myocardium [39,42,80].
Thus, in general, the results of our experiments with the LS NPRUH suggest that the basis for action of ESBAR and its analogs (histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, preductal and mildronat) is their ability to increase the affinity of the active site relative to the catecholamines, the ability to counter the desensitization of beta-AR (by reducing the activity of enzymes involved in phosphorylation beta-AP, i.e. kinase of beta -AR, protein kinases A and C), by increasing the activity of phosphatase, and the ability to restore the native structure of proteins involved in beta-AR-signaling. Results of experiments with other objects, listed below, support this idea about the mechanism of action of ESBAR and its analogues.
Influence of ESBAR and its analogs on efficiency of activation of beta-AP of other smooth muscle, myocardium and blood cells
To study the mechanism of action of ESBAR and its analogs and physiological role of ESBAR we examined the ability of blood serum as a source of ESBAR and analogues of ESBAR (histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, preductal, mildronat) for the manifestation of the effects of adrenaline on smooth muscle of the uterus of women, cow trachea, pig coronary artery, rat stomach, and myocardium of frog, rats and humans and also human blood cells – erythrocytes and platelets.
Myometrium of pregnant women: We have previously found [1,5,15] that physiological properties of isolated myometrium of nonpregnant and pregnant women differ significantly from the myometrium nonpregnant and pregnant rats [14,15], rabbits [3,15] and pigs [2,15]. It has been shown [1,15], that adrenaline increases the contractile activity (CA) of isolated myometrium nonpregnant women, due to the activation of alpha-AR, but inhibits CA of myometrium of pregnant women (due to activation of beta2-AR) and again increases CA of myometrium from partutient (due to activation of alpha-AR).In the clinical setting we have identified [7,15], that the 10-minute intravenous infusion of adrenaline (0,6 micrograms / min) to women before the onset of labor significantly reduces the numbers of uterine contractions ( from 3,2 to 2.5 for 10 minutes, or up to 76% of baseline), and its introduction into an active phase I of stage of labor is the reduction in the contraction frequency (from 3.3 to 2.9 for 10 minutes, i.e. up to 86%) was not statistically significant. Consequently, in labor's ability of adrenaline reduced of contractile activity of uterus (CAU) decreases. At the same time, in both cases adrenaline caused a statistically significant increase in maternal heart rate (corresponding up to to 124% and 113% of baseline), systolic pressure (up to 110% and 108%) and diastolic pressure (up to 110% and 112%), i.e. reaction of the cardiovascular system to the introduction of adrenaline during labor has not changed. In another study, when using outdoor hysterography set [8,15], that 5-minute intravenous infusion of beta2-adrenomimetic partusisten (0.00125 mg per minute) in pregnant women at 28-36 weeks gestation (in the absence of symptoms of threat of premature labor (TPL) significantly reducing amplitude of large waves (on 52% of the original level), frequency of contractions generation (on 47%) and the total activity (on 74%). In women in late pregnancy i.e. at time of 38-42 weeks, the same dose of partusisten causes less decrease CAU - including amplitude (on 27%) and the total activity (on 42%), while women in the active phase of the first stage of labor, the introduction of this dose is much less pronounced reduction of large amplitude waves (only on 16%) and the total activity (only on 25%). These observations suggest that before labor and during labor agonist of beta -AR partusisten even in a small dose can inhibit of the CAU. However, this ability in labor is clearly reduced, that indicating a decrease of beta-adrenoreactivity of myometrium of women in vivo. In similar studies, we have shown [15] that in pregnant women (28-36 weeks) with no signs of threat of premature labor (TPL) partusisten test, wich performed as described previously [8],inhibits background of CAU, while in pregnant women with signs of threat of premature labor (TPL) this test in some cases was negative, ie, not accompanied with inhibition of CAU. This is evidenced about the decreasing of beta- adrenoreactivity of myometrium at TPL. All these data support the notion that activation of the myometrium beta2-AR in pregnant women results in inhibition of CAU before labor and this inhibitory effect before labor is significantly reduced.
Investigation isolated myometrium of pregnant women showed [15-18,68], that the blood serum of pregnant women (in dilutions 1:50, 1: 100, 1: 500, 1: 103) and amniotic fluid (at dilutions 1:10, 1: 100, 1:500, 1: 103) did not affect the expression of the stimulating effect of adrenaline (10-7 and 10-6 g/mL), but reduce it after removal of serum or after prolonged (up to 90 min) exposure to amniotic fluid ( Figure 5). Thus, these experiments no clearly demonstrate the ability of ESBAR to enhance of beta-adrenoreactivity of pregnant women myometrium of failed. At the same time histidine (3х10-7 and 3х10-6 g/mL) and trimetazidine (preductal, 10–7 g / ml) prevented the manifestation of the stimulating effect of adrenaline, used at a concentration of 10-8 g / mL and 10-7 g /mL, as well as reversial uterostimulatory effect of adrenaline in uteroinhibitory effect (Figure 4). In other words, histidine and trimetazidine (preductal) showed (beta- adrenosensibilizatory activity. Unfortunately, such studies have not been conducted using other analogs of ESBAR - tryptophan, tyrosine and mildronat. Thus, experiments with isolated myometrium of pregnant women is not given conclusive evidence of the applicability of the hypothesis of beta-ARIM against the CAU and the participation of ESBAR in its implementation at women. At the same time, the results of our studies are consistent with the above view that pregnancy at women is accompanied by the conversion of an adrenergic mediator (replacing norepinephrine with tyrosine), which helps maintain high beta-AR activation efficiency, and thereby inhibit CAU.
Figure 5: Mechanogram of myometrium strip of pregnant woman showing β- adrenosensitizing effect of 50-fold dilution of blood serum of pregnant women (С 1:50) but not at the time of perfusion and after it. Horizontal liness under the mechanogram reflect the time of exposure to substances, including adrenaline, 10-7 g/mL (АДР-7) and blood serum in dilution 1:50 (С 1:50). Calibration — 10 mN, 10 min. From [11].
The content of ESBAR in obstetric and somatic pathologies
Judging by the effective titer of blood serum dilution, it was found that the content of ESBAR at human depends on gender (in women, especially in pregnant women is higher than in men), at pregnant women it depends from the presence of obstetric complications So, the content of ESBAR increased in preeclampsia [15,67] and the weakness of labor activity [15,67] while reducing at placental insufficiency[15,67], but not changed at threat of premature labor [15,67]. As well as in pregnant women with hypertension or vegeto-vascular dystonia. The content of ESBAR varies with somatic pathology - it was reduced at myocardial ischemia or coronary heart disease [62-64], essential hypertension [25,26,65,66], and bronchial asthma [30,31]. This indicates the involvement of ESBAR in the pathogenesis of obstetric complications and a number of somatic diseases.
Conclusion
So, summarizing of the results of 20 year studies about presence in the blood (as well as urine, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, and amniotic fluid) of endogenous modulators of adrenergic and M-cholinergic reactivity, allow us to consider them as humoral components of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The focus of this article is given to the endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptor (ESBAR). Most likely, that ESBAR is a water-soluble low molecular weight compound, and its analogs are histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, mildronat and preductal. Several dilutions of human blood serum and the analogs of ESBAR capable to increase the efficacy of activation of beta-AP of smooth muscle of the rat uterus, women uterus, pig coronary artery, cow renal artery, cow trachea, rat stomach and also beta-AP of myocardium from frog, rat and human, as well as beta-AP human erythrocytes (the action of histidine) and human platelets (under the action of tryptophan). The content of ESBAR at human depends on gender (in women, especially in pregnant women is higher than in men), at pregnant women it depends from the presence of obstetric complications and its and it varies with somatic pathology. Although the nature of ESBAR hitherto unknown and ESBAR not isolated in pure form, that it is an obstacle to recognition of its existence, but the physiological effects of ESBAR and its analogs indicate, that ESBAR playing an important role in the regulation of the activities of visceral organs and probably brain structures. In general, ESBAR and its analogs are considered to be direct modulators (urgent action) of beta1-AR and beta2-AR. In the various operating conditions of cells ESBAR and its analogs with short latency increase initial effectiveness of the activation of beta-AR or restore it if it was lowered during prolonged agonist interaction with beta-AR (i.e. at desensitization of beta-AR), or exposure adrenoblockers or when exposed to damaging factors such as ozone or LPC. It is assumed that the basis of this action of ESBAR is the ability of ESBAR or its analogs bind with amino acid site of beta-AR and thus allosterically enhance the affinity of the beta-AR to catecholamines. Simultaneously ESBAR and its analogs are likely to inhibit the phosphorylation of beta-AR (possibly due to inhibition of kinase of beta-AP, proteinkinase A and proteinkinase C) and accelerate the dephosphorylation of beta-AR by activating phosphatase, and (like chaperones) restore the native protein structure involved in the beta-AR-induced signaling. This is obvious evidence of the need for a more thorough study of these provisions and the selectivity with respect to different populations of beta-AR (beta1-AR, beta2-AR and beta3-AR). Substantiates the notion that prevents of desensitization of beta-AR, ESBAR promotes the functioning of the beta-adrenergic inhibitory mechanism (beta-ARIM) in pregnant women, necessary for inhibition of contractile activity of uterus (CAU). This function of ESBAR is realized by involving adrenergic terminals which are supposed to occur conversion mediator at during pregnancy, i.e. instead of adrenaline or noradrenaline tyrosine temporaril becomes of mediator. Therefore ESBAR and its analogs can play an important role in the prevention of preterm labor. ESBAR involved in the regulation of activity of the heart, circulatory system and respiratory tracts. Therefore deficiency of ESBAR- content may be a cause of myocardial ischemia (coronary heart disease), essential hypertension or bronchial asthma, and the use of ESBAR and its analogs may be a promising method for the prevention and treatment of these pathologies, as well as such a formidable status as heart failure. It is alleged that the heart rate variability (HRV) reflects not only the state of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), as is commonly believed, but also reflects of the blood levels of endogenous modulators, including ESBAR. We believe that the selection ESBAR in its pure form, the development of reliable and affordable method for determining the content of ESBAR, creating unique arsenal analogs of ESBAR and study of the possibility and feasibility of clinical application - all this is an important tasks for future research.
Core tip
In humans and animals there are factors that significantly modulate the efficiency of activation of beta- and alpha- adrenergic receptors, as well as the M-cholinergic receptors. Although these endogenous modulators (sensitizers and blockers) has not yet been isolated in pure form, but their physiological effects are very pronounced. The main purpose of our review - to draw attention to these factors, and, above all, to the endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptor (ESBAR). This factor, as well as its analogs (histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, preductal, mildronat) is capable s able to restore the effectiveness of the activation of beta-adrenergic receptors, reduced under the influence of various effects, including at heart failure.
Tsirkin VI, Sizova EN, Polezhaeva TV, Khlybova SV, Morozova MA, Truhin AN, Korotaeva YV, Khodyrev GN. Endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptors (ESBAR) and its analogs (review).
References
- Tsirkin VI, Sashenkov SL, Filimonov VG, Medvedev BI, Anisimov Klu. [Functional assessment of the isolated myometrium of nonpregnant and pregnant women and parturients]. Akush Ginek.1981; 12: 33-36. Ref.: https://goo.gl/V331G4
- Tsirkin VI. Сontractile properties of smooth muscle cells of the horn, cervix and broad ligament of the pig uterus. Fiziol Zh SSSR Im IM Sechenova. 1986; 72: 818-829. Ref.: https://goo.gl/nysMbB
- Tsirkin VI. The physiological properties of the smooth muscles of the vagina and uterine cornua and cervix of the rabbit. Fiziol Zh Im IM Sechenova. 1986; 32: 436-442.
- Tsirkin VI. Physiological properties of smooth muscle of the cervix uteri in the rat. Fiziol Zhl SSSR Im IM Sechenova. 1986; 72: 1635-1642. https://goo.gl/bvj54j
- Tsirkin VI, Medvedev BI, Filimonov VG, Plekhanova LM. Effect of prostaglandins on the contractile activity of isolated human myometrium. Akush Ginek. 1986: 9: 54-58. Ref.: https://goo.gl/5ifKCR
- EHL'DER MG, Hendriks CH. Preterm labor: Translate from Englisg. Moskva; Izdatel'stvo Medicina. 1984: 1- 303.
- Tsirkin VI., Medvedev BI, Plekhanova LM, Rybalova LF, Shajmardanov HA. The role of the β-adrenergic receptor-inhibitory mechanism in the regulating the contracitile activity of the human uterus. Akush. Ginekol. 1986; 1: 19-22. Ref.: https://goo.gl/2eRYpt
- Medvedev BI, Tsirkin VI, Pomaskin IN. Changes in strength of β-adrenoreceptor inhibiting mechanism on the eve of and during labor, determined by the partusisten test. Akush Ginekol. 1989; 11: 24-27. Ref.: https://goo.gl/7xkXjv
- Pomaskin IN, Medvedev BI, Tsirkin VI, Zakharov VV. Endogenous β-adrenomimetic substance as constituent of the beta adrenoreceptor-inhibiting mechanism. Akush Ginekol. 1989; (6): 23-27. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ectW5m
- Bordunovskaya VP, Tsirkin VI, Sashenkov SL. Desensitization of isolated rat myometrium to biologically active substances. Fiziol Zh Im IM Sechenova. 1981; 67: 390-397. Ref.: https://goo.gl/U4XgtP
- Zhu W, Petrashevskaya N, Ren S, Zhao A, Chakir K, et al. Gi-biased β2AR signaling links GRK2 upregulation to heart failure. Circ Res. 2012; 110: 265-274. Ref.: https://goo.gl/6zQQch
- Fu Q, Kim S, Soto D, De Arcangelis V, Di Pilato L, et al. A long lasting β1 adrenergic receptor stimulation of cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) signal in cardiac myocites. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 14771-1481. Ref.: https://goo.gl/AVFZgg
- Chakraborti S, Roy S, Chowdhury A, Mandal A, Chakraborti T. Role of PKCα-p38 MAPK-Giα axis in peroxynitrite-mediated inhibition of β-adrenergic response in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Cell Signal 2013; 25: 512-526. Ref.: https://goo.gl/gZzUit
- Peshikov VL, Tsirkin VI. Regulation of alpha- and beta-adrenoreceptor activity in the myometrium. Akush Ginekol. 1977; 2: 51–53. Ref.: https://goo.gl/M9YMSx
- Tsirkin VI, Dvoryanskij SA. Uterine activity (regulatory mechanisms). Kirov: Kirovskij gosudarstvenyj medicinskij institute. 1997: 1-270.
- Tsirkin VI, Dvoryanskij SA, Nozdrachev AD, Bratukhina SV, Morozova MA, et al. Adrenomodulatory effects of human a blood, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, saliva, and amniotic fluid. Dokl Akad Nauk. 1997; 352: 124-126.
- Tsirkin VI, Dvoryanskij SA, Dzhergeniya SL, Bratukhina SV, Neganova MA, et al. Beta-adrenomimetic and beta-adrenomodulating properties of human urine. Fiziol Cheloveka. 1997; 23: 85-92. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Jed4uq
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Dvoryanskij SA, Bratukhina SV, Morozova MA, et al. Endogenous sensitizer of β-adrenergic receptor. Vestnik Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta. Seriya 3. Biologiya. 1997; 1: 74-84.
- Tsirkin VI, Dvoryanskij SA, Nozdrachev AD, Zaugol'nikov VS, Sizova EN. Increase in beta-adrenoreactivity of coronary arteries expoused to blood serum. Dokl Akad Nauk. 1996; 351: 565-566. Ref.: https://goo.gl/eyjkUw
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Kostyaev AA, Utemov SV. Effect of ozonated Krebs solution on the tonic activity and b-adrenoreactivity of pig coronary artery smooth muscle. Rossijskij kardiologicheskij zhurnal. 2002; (6/38): 66-71.
- Sizova EN, Nozdrachev AD, Tsirkin VI, Kostyaev AA, Dvoryanskij SA, et al. Effect of ozonated Krebs on contractile activity and adrenoreactivity various smooth muscles. Vestnik Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta. Seriya 3 (biologiya). 2004; 2: 47-57.
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Sizova EN, Dvoryanskij SA, Sazanova ML. The system of endogenous modulators involved in the control of functioning of peripheral autonomic nervous structures. Dokl Akad Nauk 2002; 383: 112-115. Ref.: https://goo.gl/AF3zad
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Sazanova ML, Dvoryanskij SA, Khlybova SV. Uteroactive, beta-adrenomodulating, and M-cholinomodulating properties of the human umbilical blood serum. Dokl Biol Sci 2003; 388: 31-34. Ref.: https://goo.gl/aBQBap
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Sazanova ML, Dvoryanskij SA. Physiological characteristics of myocytes of the human umbilical arteries and vein and the effect of umbilical blood serum on them. Dokl Biol Sci. 2003; 388: 15-17. Ref.: https://goo.gl/cm5wiA
- Penkina YuA, Demina NL, Kashin AYu, Tsirkin VI, Tarlovskaya EI, et al. The role of endogenous modulators of adrenoreactivity in the pathogenesis of arterial hypertension. Ural'skij medicinskij zhurnal. 2007; (7/35): 88- 94.
- Demina NL, Tsirkin VI, Tarlovskaya EI, Kashin RYu. Alpha- and beta-adreno-, M-cholinemodulatory activity of serum at patients with arterial hypertension. Kardiovaskulyarnaya terapiya i profilaktika. 2008; 2: 16-22.
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Kashin RYu. The modulation efficiency alpha-adrenoceptor activation of smooth muscle of the cow renal artery. Dokl Akad Nauk. 2009; 425: 561-566.
- Kashin RYu, Nozdrachev AD, Tsirkin VI. The modulation of contractile response of the cow renal artery smooth muscle on adrenergic, cholinergic and depolarizing impacts. Vestnik Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta Ser. 3 (biologiya). 2010; 1: 55-71.
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Kostyaev AA. Effect of ozonated Krebs solution on the tonic activity and beta-adrenoreactivity of cow tracheal smooth muscle. Uspekhi sovremennogo estestvoznaniya. 2003; 6: 23-27.
- Tsirkin VI, Kononova TN, Sizova EN, Popova IV, Vahrusheva AS. The possible role of endogenous modulators of beta-adreno- and M-cholinoreactivity in the pathogenesis of bromchial asthma. Pul'monologiya. 2007; 5: 46-50.
- Tsirkin VI, Kononova TN, Sizova EN, Vakhrusheva AS, Popova IV. Changing of the beta-adrenergic and M-cholinergic modulating activity of blood serum and urine in brachial asthma. Fiziol Cheloveka. 2008; 34: 137-140. Ref.: https://goo.gl/6fGuJ3
- Kunshin AA, Nozdrachev AD, Tsirkin VI, Trukhina SI, Dvoryanskij SA, et al. Effect of human serum on M-choline- and alpha-, beta-adrenoreactivity of the rat stomach smooth muscle. Vestnik. Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta. Ser. 3(biologiya). 2007; 3: 40-53.
- Gulyaev PV, Pomaskina TV, Kunshin AA, Chervotkina LA, Gulyaeva SF, et al. Mechanism of action of Nizhne-Ivkinskaya 2K sulfate-calcium mineral water in combined treatment of acid-dependent gastrointestinal diseases. Ter Arkhiv. 2008; 80: 23-28. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qRW5yr
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Trukhin AN, Sizova EN. Effects of endogenous modulators of beta-adrenergic and cholinergic receptors on heart rate variability. Dokl Biol Sci. 2004; 394: 16-19. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9sLxyP
- Trukhin AN, Tsirkin VI, Sizova EN. Histidine increases beta-adrenoreactivity of myocardium in frogs. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2004; 138: 123-126. Ref.: https://goo.gl/U7bK32
- Penkina YA, Tsirkin VI, Prokazova NV. Effect of histidine on the beta -adrenoceptor blocking effect of lysophosphatidylcholine in experiments with isolated frog and rat myocardium. Vestnik Pomorskogo universiteta. Seriya «Fiziologicheskie i psihologo-pedagogicheskie nauk. 2007; (2/12): 19 -25.
- Penkina YA, Nozdrachev AD, Tsirkin VI. Effect of human blood serum, histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, mildronat and lysophosphatidylcholine on inotropic effect of adrenaline in the experiments with the frog and rat myocardium. Vestnik Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta. Seriya 3 (Biologiya). 2008; 1: 55-68.
- Tsirkin VI, Korotaeva YV. Effect of pregnant women blood serum on the adrenoreactivity of right ventricular of rat heart, decreased beta-blockers. Vestnik Severnogo (Arkticheskogo) federal'nogo universiteta. Seriya «Mediko-biologicheskie nauki. 2013; 4: 77–88. Ref.: https://goo.gl/hsMWLh
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Korotaeva YV. An endogenous sensitizer of β- adrenergic receptors and its analogs attenuate the inhibition of β- adrenergic receptors by propranolol and atenolol in the rat myocardium. Dokl Biol Sci. 2014; 456: 169-172. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ghAFr9
- Tsirkin VI, Korotaeva YV. Influence of hystidine, tryptophan and tyrosine on contractility and adrenoreactivity of right ventricle myocardial of nonpregnant rats. Vestnik Cevernogo (Arkticheskogo) federal'nogo universiteta. Seriya. Mediko-biologicheskie nauki. 2014; (3): 79-90. Ref.: https://goo.gl/V4a38F
- Korotaeva YV, Tsirkin VI. The negative inotropic effect of adrenaline is not associated with the activation of beta1-, beta2-, alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoreceptors. Vestnik Nizhegorodskogo universiteta im NI Lobachevskogo. 2014; (4/1): 193-197.
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Korotaeva YV. The effect of histidine on the contractility and adrenoreactivity of the myocardium of nonpregnant and pregnant rats. Dokl Biol Sci. 2015; 460: 12-16. Ref.: https://goo.gl/p6QCnx
- Popova OV, Trukhina SI, Tsirkin VI. Effect of histamine on the heart rate variability and electrical activity of the brain. Vestnik Novosibirskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta. Seriya: biologiya i klinicheskaya medicina. 2010; 8 4: 107-112.
- Korotaeva KN, Vyaznikov VA, Tsirkin VI, Kostyaeva AA. Influence of the human blood serum on contractility and beta-adrenoreactyvity of the isolated human myocardium. Fiziol. Cheloveka. 2011; 37: 83-91. Ref.: https://goo.gl/hSfJS4
- Korotaeva KN, Nozdrachev AD, Vyaznikov VA, Tsirkin VI. Effect of tyrosine, histidine, tryptophan, mildronat and human serum on the amplitude of caused contractions of human cardiomyocytes and inotropic effect of adrenaline. Vestnik Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta. Ser. 3 (biologiya). 2011; 2: 45-57.
- Volodchenko AI, Tsirkin VI. Effect of propranolol, histidine, and trimethylhydrazine propionate on the capacity of epinephrine to change the rate of erythrocyte agglutination. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2014; 157: 592-596. Ref.: https://goo.gl/78XcqG
- Nozdrachev AD, Tumanova TV, Dvoryanskij SA, Tsirkin VI, Darmov IV, et al. Activity of a series of amino acids as potential sensitizers of smooth muscle beta-receptors. Dokl Akad Nauk 1998; 363: 133-136. Ref.:© https://goo.gl/fVfn9X
- Tsirkin VI, Sizova EN, Podtetenev AD, Bratchikova TV, Anisimova OV, et al. Trimetazidine and mildronat as direct sensitizers of the β2-adrenergic (experimental evidence) Rossijskij kardiologicheskij zhurnal. 2002; (1/33): 45-52.
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Podtetenev AD, Bratchikova TV, Dvoryanskij SA, et al. Ability of trimetazidine (preductal) and mildronat have a direct β-adrenergic sensitizing effect on smooth muscle. Message 2. Rossijskij kardiologicheskij zhurnal. 2002; (2/34): 50-56.
- Tsirkin VI, Dvoryanskij SA, Sizova EN, Anisimova OV, Trukhin AN, et al. Ability of trimetazidine (preductal) and mildronat have a direct β-adrenergic sensitizing effect on smooth muscle. Vestnik Rossijskogo universiteta druzhby narodov. Ser. Medicina, Akusherstvo i Ginekologiya 2002; 1: 219- 225.
- Tsirkin VI, Sizova EN, Tumanova TV, Kostyaev AA. The ability of an endogenous sensitizer of β-adrenergic receptor (ESBAR) and its analogs - histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, preductal and mildronat reduce β-adrenoceptor blocking effect of ozone. Uspekhi sovremennogo estestvoznaniya. 2003; 4: 60-61.
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Dvoryanskij SA, Kostyaev AA. Changes of contractile activity and β-adrenoreactivity of isolated pregnant women myometrium under the influence of ozonated Krebs solution. Uspekhi sovremennogo estestvoznaniya. 2004; 1: 15-19.
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Tumanova TV, Kostyaev AA. The ability of the histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, trimetazidine, mildronat and the blood serum reduce of β-adrenoceptor blocking effect of ozone. Sovremennye naukoemkie tekhnologii. 2004; 3: 21-26.
- Khlybova SV, Tsirkin VI, Dvoryanskij SA. The content of histidine in the blood serum of women in physiological gestational process and at the number of obstetric complications. Zhurnal akusherstva i zhenskih boleznej. 2006; 55: 50-54.
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Tumanova TV. Influence of amino acids alimentary on contracts ability in beta-adreno- and M-cholinoreactivity of smooth muscles. Vopr Pitan 2008; 77: 26-32. Ref.: https://goo.gl/fMZZDr
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Toropov AL. An endogenous sensitizer of β-adrenergic receptors and its analogs in the experiments with rat myometrium reduce the β-adrenoblocking effect of obzidan. Dokl Biol Sci. 2010; 435: 375-380. Ref.: https://goo.gl/UrW5RK
- Popova OV, Tsirkin VI, Nureev IT, Zlokazova MV, Trukhina SI. Effect of mildronat on the central nervous system of students with symptoms of attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity. Vestnik Nizhegorodskogo universiteta im NI Lobachevskogo. Seriya biologiya. 2010; 6: 105-112.
- Toropov AL, Nozdrachev AD, Tsirkin VI. Investigation of the mechanism of action of endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenoceptor (ESBAR) and its analogs. Vestnik Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta, Ser. 3 (biologiya). 2011; ): 27-42.
- Toropov AL, Tsirkin VI, Kostyaev AA. Combined effects of blood serum as a source of endogenous β-adrenoceptor-sensitizing agent and its analogues histidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, mildronat, and preductal. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2011; 151: 84-87. Ref.: https://goo.gl/YJKWUS
- Korotaeva KN, Tsirkin VI, Vyaznikov VA. Positive inotropic effect of tyrosine, histidine, and tryptophan in experiments on isolated human myocardium. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2012; 153: 51-53. Ref.: https://goo.gl/D1k8xT
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Sizova EN, Tumanova TV. Physiological characteristics of endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptors (ESBAR) and its putative components. Dokl Biol Sci. 2004; 398: 363-366. Ref.: https://goo.gl/KTHksq
- Mal'chikova SV, Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Gulyaeva SF, Trukhin AN, et al. Beta-adrenergic sensitizing activity of blood serum in patients with acute coronary incident, and the influence of physical training. Rossijskij kardiologicheskij zhurnal. 2003; (3/41): 33 –39.
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Sizova EN, Mal'chikova SV, Gulyaeva SF. Effect of physical training on blood level of endogenous modulators of beta-adreno- and M-cholinoreactivity in patients with a history of myocardial infarction. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2003; 136: 14-18. Ref.: https://goo.gl/WGeAQM
- Mal'chikova SV, Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Gulyaeva SF, Trukhin AN, et al. Changing of the β-adrenosensitatory and M- anticholinergic activity of blood serum in older adults with acute coronary event, and under the influence of physical training Kardiovaskulyarnaya terapiya i profilaktika. 2003; 2: 36-43.
- Demina NL, Tsirkin VI, Tarlovskaya EI, Kostyaev AA. Alpha –adrenomodulatory activity of blood serum in arterial hypertension. Rossijskij kardiologicheskij zhurnal. 2008; (1/69): 65-70.
- Tsirkin VI, Nozdrachev AD, Khlybova SV, Demina NL. The content in the blood serum of endogenous modulators of adrenoreactivity and endogenous activator of myocyte contractility as a reflection of their participation in the regulation of blood pressure. Vestnik Sankt-Peterburskogo universiteta, seriya 3 (Biologiya). 2008; 2: 69 – 82.
- Khlybova SV, Tsirkin VI, Dvoryanskij SA, Ezhov AV, Roman VV, et al. β-Adrenosensibilizatory activity of blood serum and the contents in serum hystidine, tryptophan, tyrosine, and other free amino acids in women with physiological and complicated pregnancy and labor. Vyatskij medicinskij vestnik. 2007; (2-3): 112-121.
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI. The physiological characteristics of the endogenous modulators of β-adreno- and M-choline reactivity. Kirov: Vyatskij social'no-ehkonomicheskij institute. 2006: 1-183.
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Tumanova TV, Sazanov AV. The impact of a number of drugs on the β-adreno- and M-cholinoreactivity of rat myometrium. Vyatskij medicinskij vestnik. 2004; 1: 25-31.
- Tumanova TV, Darmov IV, Drobkov VI, Tsirkin VI, Dvoryanskij SA. Effect of amino acids on the contractile activity and beta-adrenoreactivity of the myometrium. Vestnik Vyatskogo peduniversiteta. 1997; 2: 20-21.
- Toropov AL, Korotaeva KN, Samodelkina EO, Tsirkin VI, Vyaznikov VA. Effect of lysophosphatidylcholine on adrenero- and M-cholinoreactivity of smooth muscle and myocardium. Vestnik Novosibirskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta Seriya: Biologiya, klinicheskaya medicina. 2010; 8: 18-26.
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Tumanova TV. Investigation of the effect of 20 amino acids at the β2-adrenо - and M1-cholinoreactivity of rat myometrium. Vyatskij medicinskij vestnik. 2003; 4: 80-85.
- Shalyapina VG, Rakitskaya VV, Abramchenko VV. Adrenergic innervations of uterus. Leningrad: Nauka. 1988. 1-143.
- Rakitskaya VV, Chudinov IuV, Shalyapina VG. The adrenergic innervation of the normal rat uterus and during pregnancy. Fiziol Zh SSSR Im IM Sechenova. 1990; 76: 1251–1259. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FkwFQG
- Tumanova TV, Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI. Ability of L-histidine to decrease desensitization of the myometrium to epinephrine. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2004; 138: 321-324. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qZX1Ah
- Woodall MC, Ciccarelli M, Woodall BP, Koch WJ. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2: a link between myocardial contractile function and cardiac metabolism. Circ Res. 2014; 114: 1661-1670. Ref.: https://goo.gl/nGhq8H
- Sizova EN, Tsirkin VI, Kostyaev AA. Effect of ozone exposure on contractile activity and chemoreactivity of uterus horns longitudinal muscles of nonpregnant rats. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2003; 89: 427-435. Ref.: https://goo.gl/YPKgEP
- Prokazova NV, Zvezdina ND, Suslova IV, Korotaeva AA, Turpaev TM. Effect of lysophasphatidylcholine on sensitivity of the heart to acetylcholine and binding of quinuclidinyl benzilate to myocardial membranes. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova.1998; 84: 969-978. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FaMU4F
- Mashkovskij MM. Drugs. V dvuh tomah. Tom 2.14-th ed. Moskva: Novaya volna. 2000: 168-169.
- Korotaeva YV, Tsirkin VI. Endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptors (ESBAR) and its analogs are antagonists of beta-blockers. Vyatskij medicinskij vestnik. 2013; 3: 24-30.