Abstract
Research Article
Awareness of Myocardial Infarction in Nangarhar Residents: A Community Based Study
Akmal Shams, Ikramullah Ibrahimi* and Hayatullah Ahmadzai
Published: 27 August, 2024 | Volume 9 - Issue 2 | Pages: 130-134
Myocardial infarction is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The overall aim of the study was to evaluate community awareness about myocardial infarction.
It was a community-based cross-sectional study conducted during one month including both male and female participants aged 18 years and over in Nangarhar province of Afghanistan.
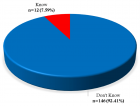
The percentage of awareness for risk factors was as follows: Diabetes (56.4%), Hypertension (43.4%), Elderly (42.1%), Obesity (39.8%), Physical inactivity (38.5%), Hyperlipidemia (37.6%), and Family history (33.8%). Furthermore, knowledge about symptoms and signs was as the following: chest pain (67.4%), pain in neck and jaw (57.8%), Dyspnea (50.7%), pain in arms (46.1%), weakness/fainting (40.1%), cold sweats (38.2%), nausea and vomiting (34.5%), anxiety (29.6%), fever (22.7%), hypotension/shock (20.1%), and silent myocardial infarction (11.3%). Moreover, 24% of participants did not know about the prevention strategies for myocardial infarction. Regarding treatment, 80.3% of participants exactly knew to go to the emergency room, 11.9% of participants would intend to go to a general practitioner (GP), 5.6% of participants would ask others for advice on what to do, and 2.2% of participants would wait to see if the symptoms go away spontaneously or if the symptoms were due to other diseases.
The current awareness level about myocardial infarction especially atypical symptoms, risk factors, prevention, and treatment strategies in Nangarhar residents was insufficient, especially in females and healthy individuals, and warrants designing and implementing immediate awareness programs in order to avoid delay of treatment-seeking, misbeliefs about the disease and subsequent morbidity and mortality.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001193 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Awareness; Myocardial infarction; Knowledge; Afghanistan
References
- Massahikhaleghi P, Tehrani-Banihashemi A, Saeedzai SA, Hossaini SM, Hamedi SA, Moradi-Lakeh M, et al. Burden of diseases and injuries in Afghanistan, 1990–2016: Findings from the global burden of disease 2016 study. Arch Iran Med. 2018;21(8):324-334. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30113853/
- Berkman ND, Sheridan SL, Donahue KE, Halpern DJ, Crotty K. Low health literacy and health outcomes: An updated systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(2):97–107. Available from: https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-2-201107190-00005
- Khan MS, Jafary FH, Faruqui AM, Rasool SI, Hatcher J, Chaturvedi N, et al. High prevalence of lack of knowledge of symptoms of acute myocardial infarction in Pakistan and its contribution to delayed presentation to the hospital. BMC Public Health. 2007;7:284. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-7-284
- Lu L, Liu M, Sun RR, Zheng Y, Zhang P. Myocardial infarction: Symptoms and treatments. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;72(3):865-867. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0553-4
- Whitaker S, Baldwin T, Tahir M, Choudhry O, Senior A, Greenfield S. Public knowledge of the symptoms of myocardial infarction: A street survey in Birmingham, England. Fam Pract. 2012;29(2):168-173. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/fampra/cmr079
- Khabti S, Alsaeeri A, Alkhathami M, Alsuayri M, Alghamdi K, Alshahrani A, et al. Community awareness of myocardial infarction in Bisha region, Saudi Arabia. Int J Med Dev Ctries. 2023;7(September 2022):13-19. Available from: https://ijmdc.com/?mno=118580
- Park KS. Factors affecting awareness of myocardial infarction symptoms among the general public in Korea. Epidemiol Health. 2020;42. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2020032
- Tran P, Mittleman MA. Assessing the associations between awareness of myocardial infarction symptoms, socioeconomic factors, and cardiovascular disease risk factors through regression models. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2017;4(5):957-966. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-016-0299-8
- Karki KC, Pandey A. Awareness regarding myocardial infarction among diabetic patients attending in a tertiary level hospital. Acta Sci Med Sci. 2019;3(8):131-136. Available from: https://actascientific.com/ASMS/pdf/ASMS-03-0359.pdf
- Alsaab SM, Almutairi AM, Alsaadi GK, Altokhais ZA, Alabdulqader SH, Alnofal WY, et al. Awareness of myocardial infarction symptoms and risk factors in Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study. Cureus. 2023; 15(12). Available from: https://doi.org/10.7759%2Fcureus.50092
- Hertz JT, Madut DB, Tesha RA, William G, Simmons RA, Galson SW, et al. Knowledge of myocardial infarction symptoms and perceptions of self-risk in Tanzania. Am Heart J. 2019;210:69-74. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2019.01.003
Figures:
Similar Articles
-
Left Atrial Remodeling is Associated with Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with Reperfused Acute Myocardial InfarctionChristodoulos E. Papadopoulos*,Dimitrios G. Zioutas,Panagiotis Charalambidis,Aristi Boulbou,Konstantinos Triantafyllou,Konstantinos Baltoumas,Haralambos I. Karvounis,Vassilios Vassilikos. Left Atrial Remodeling is Associated with Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with Reperfused Acute Myocardial Infarction. . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001001; 1: 001-008
-
Procedure utilization, latency and mortality: Weekend versus Weekday admission for Myocardial InfarctionNader Makki,David M Kline,Arun Kanmanthareddy,Hansie Mathelier,Satya Shreenivas,Scott M Lilly*. Procedure utilization, latency and mortality: Weekend versus Weekday admission for Myocardial Infarction. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001008; 2: 020-025
-
Spontaneous rupture of a giant Coronary Artery Aneurysm after acute Myocardial InfarctionOğuzhan Çelik,Mucahit Yetim,Tolga Doğan,Lütfü Bekar,Macit Kalçık*,Yusuf Karavelioğlu. Spontaneous rupture of a giant Coronary Artery Aneurysm after acute Myocardial Infarction. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001009; 2: 026-028
-
A rare Congenital Coronary Artery Anomaly: Woven Right Coronary Artery associated with Myocardial InfarctionTolga Doğan,Mucahit Yetim,Lütfü Bekar,Oğuzhan Çelik,Macit Kalçık*,Yusuf Karavelioğlu. A rare Congenital Coronary Artery Anomaly: Woven Right Coronary Artery associated with Myocardial Infarction. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001013; 2: 050-051
-
Assessment of risk factors and MACE rate among occluded and non-occluded NSTEMI patients undergoing coronary artery angiography: A retrospective cross-sectional study in Multan, PakistanIbtasam Ahmad,Muhammad Haris,Amnah Javed,Muhammad Azhar*. Assessment of risk factors and MACE rate among occluded and non-occluded NSTEMI patients undergoing coronary artery angiography: A retrospective cross-sectional study in Multan, Pakistan. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001023; 3: 023-030
-
Use of Rivaroxaban and Apixaban, Two Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs), in Renally Impaired Patients - the limits of our knowledgeKenneth T Moore*,Maria Langas. Use of Rivaroxaban and Apixaban, Two Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs), in Renally Impaired Patients - the limits of our knowledge. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001026; 3: 049-051
-
An observational study of the occurrence of anxiety, depression and self-reported quality of life 2 years after myocardial infarctionCatrin Henriksson,Mona-Lisa Wernroth,Christina Christersson*. An observational study of the occurrence of anxiety, depression and self-reported quality of life 2 years after myocardial infarction. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001027; 3: 052-063
-
Is there an ideal blood pressure during cardiopulmonary bypass to prevent postoperative cerebral injury? – What does the recent evidence say?Ahmed Zaky*. Is there an ideal blood pressure during cardiopulmonary bypass to prevent postoperative cerebral injury? – What does the recent evidence say?. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001031; 3: 104-105
-
Diagnostic accuracy of TIMI versus GRACE score for prediction of death in patients presenting with Acute Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI)Syed Haseeb Raza Naqvi,Tariq Abbas,Han Naung Tun*,Ali Ahmad Naqvi,Zubair Zaffar,Badar ul Ahad Gill,Nisar Ahmad. Diagnostic accuracy of TIMI versus GRACE score for prediction of death in patients presenting with Acute Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI). . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001032; 4: 001-005
-
Impact of the Israeli attacks at 2014 on incidence of STEMI in GazaMohammed Habib*,Belal Aldabbour. Impact of the Israeli attacks at 2014 on incidence of STEMI in Gaza. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001037; 4: 036-037
Recently Viewed
-
Trends in TeledentistryRudrakshi C*. Trends in Teledentistry. J Clin Adv Dent. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcad.1001014; 4: 004-005
-
Au26-35: A Special Geometrical Structure of Au33 (D2) Cluster with Highly Occupied - 14 Pairs of Double-State DegeneracyK Vishwanathan*. Au26-35: A Special Geometrical Structure of Au33 (D2) Cluster with Highly Occupied - 14 Pairs of Double-State Degeneracy. Ann Adv Chem. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.aac.1001035; 6: 063-080
-
Texture of Thin Films of Aluminum Nitride Produced by Magnetron SputteringStrunin Vladimir Ivanovich,Baranova Larisa Vasilievna*,Baisova Bibigul Tulegenovna. Texture of Thin Films of Aluminum Nitride Produced by Magnetron Sputtering. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001106; 8: 013-016
-
Minimising Carbon Footprint in Anaesthesia PracticeNisha Gandhi and Abinav Sarvesh SPS*. Minimising Carbon Footprint in Anaesthesia Practice. Int J Clin Anesth Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcar.1001025; 8: 005-007
-
On Friedman equation, quadratic laws and the geometry of our universeS Kalimuthu*. On Friedman equation, quadratic laws and the geometry of our universe. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001041; 4: 048-050
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."