Abstract
Retrospective Study
Lifestyle modification practice and associated factors among diagnosed hypertensive patients in selected Hospitals in West Arsi Zone, Oromia Regional State, Ethiopia
Hika Wakjira*, Tesfaye Gobena and Hirbo Shore
Published: 01 February, 2022 | Volume 7 - Issue 1 | Pages: 006-012
Background: Globally 1.13 billion people were living with hypertension, Out of this two-thirds of them were living in low and middle-income countries. In Ethiopia, Non-Communicable Disease deaths are estimated at around 42%. However, it remains widely undetected and poorly controlled. To resolve these, lifestyle modification approaches that are often overlooked are the cornerstone of the prevention and management of hypertension.
Objective: To assess lifestyle modification practice and associated factors among hypertensive patients in selected hospitals in West Arsi Zone, Oromia Regional, Ethiopia December 7 to 21, 2019.
Method: Hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted in the selected public hospital among 299 hypertensive patients. Systemic random sampling methods were used to select the study participants. Data were collected by face-to-face interviews using a structured questionnaire by trained data collectors. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and multivariate logistic regression method to identify predictors of the outcome (p < 0.05).
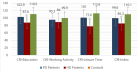
Results: Of the total participants, only 25.2% (95% CI: 18.8-32.9) of the patients were practiced recommended lifestyle modifications. Patients Age older than 65 years (AOR = 2.9, 95% CI: 1.17 - 7.0), the patients with 2-5 years’ time since diagnosed hypertension (AOR = 0.26, 95% CI: 0.07 - 0.9), multiple co-morbidity (AOR = 2.7, 95% CI: 1.25 - 5.8,) and their knowledge on hypertension management (AOR = 14.6, 95% CI: 4.6 - 45.9) have an independently associated with recommended lifestyle modification.
Conclusion: Lifestyle modification practices among hypertensive patients were low in this study. Age, comorbidity, time since diagnoses of hypertension, and knowledge of lifestyle were identified as predictors of the outcome.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001124 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Lifestyle modification; Hypertension; Practices; Ethiopia
References
- American Heart Association. Guideline for the Prevention, detection, evaluation and management of high Blood Pressure in adults. 2017.
- Clinical guidelines for the management of hypertension. 2005.
- Joint TS. prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressur. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- World Health Organization. A global brief on hypertension. 2013.
- National strategic action plan for the prevention and control of NCDs in Ethiopia 2014 - 2016. 2014.
- Abu H, Aboumatar H, Carson K, Goldberg R, Cooper LA. Hypertension knowledge, heart healthy lifestyle practices and medication adherence among adults with hypertension. Eur J Pers Cent Healthc. 2018; 6: 108-114. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32405420/
- Mengistu D, Tibebu A. Negesa L. Adherence to recommended lifestyle modifications and factors associated for hypertensive patients attending chronic follow-up units of selected public hospitals in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Patient Prefere Adherence. 2017; 11: 323-330. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28280305/
- WHO STEP wise Approach to Chronic Disease Risk-Factor Surveillance. 2016.
- Siyum E, Kelbiso L, Olana R. Lifestyle modification practice and associated factors among diagnosed hypertensive patients in selected hospitals, South Ethiopia. Clin Hypertens. 2017; 23: PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29214054/
- Afia FAM, Owusu-Daaku FT, Addo MO, Saana II. Ghanaian hypertensive patients understanding of their medicines and life style modification for managing hypertension. Int J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci. 2014; 6: 165-170.
- Tahmina, Habib N, Kailash K, Rashid M. Lifestyle modification practice in rural community at Kedah in Malaysia. J Basic, Clin Appl Health Sci. 2018; 1: 19-26.
- Lipilekha P, Kalyan K, Sumitra P, Trilochan S. Lifestyle Pattern and Hypertension Related Knowledge, Attitude and Practices among Diagnosed Patients of Hypertension Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital. J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 2017; 8: 108-111.
- Zahid HM, Most L, Satya P, Marif. Knowledge, attitude and practice of life style modification in the management of hypertension. Obese Eat Disorder.2017; 3:
- Lama A, Alshimaa A, Maradi A, Rana M. Awareness and Knowledge on Hypertension and its Self-Care Practices Among Hypertensive Patients in Saudi Arabia. Ann Int Med Dent Res. 2017; 3: 58-63.
- Abubaker E. Level of Adherence to Lifestyle Changes And Medications Among Male Hypertensive Patients In Two Hospitals In Taif; Kingdom Of Saudi Arabia. Int J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci. 2015; 7: 168-172.
- Yirga L, Seid I, Kassa TD, Asgedom SW. Practice and predictors of self-care behaviors among ambulatory patients with hypertension in Ethiopia. PLoS ONE. 2019; 14: 1-16. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31242265/
- Durai V, Rani MA. Knowledge and Practice on lifestyle modifications among males with hypertension. Indian J Commun Health. 2015 27: 143-149.
Figures:
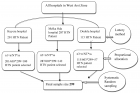
Figure 1

Figure 2
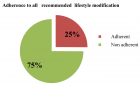
Figure 3
Similar Articles
-
Short and Medium-Term Evaluation of Patients in Coronary Post-Angioplasty: Préliminary results at the Cardiology Department of the Hospital University Aristide Le Dantec of Dakar (Senegal): Study on 38 CasesDioum M*,Aw F,Masmoudi K,Gaye ND,Sarr SA,Ndao SCT, Mingou J,Ngaidé AA,Diack B,Bodian M,Ndiaye MB,Diao M,Ba SA. Short and Medium-Term Evaluation of Patients in Coronary Post-Angioplasty: Préliminary results at the Cardiology Department of the Hospital University Aristide Le Dantec of Dakar (Senegal): Study on 38 Cases. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001006; 2: 008-012
-
Indications and Results of Coronarography in Senegalese Diabetic Patients: About 45 CasesNdao SCT*,Gaye ND,Dioum M,Ngaide AA,Mingou JS,Ndiaye MB, Diao M,Ba SA. Indications and Results of Coronarography in Senegalese Diabetic Patients: About 45 Cases. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001007; 2: 013-019
-
Non-hemodynamic factors associated to the risk of developing hypertensive cardiopathyAlexis Álvarez-Aliaga*,Julio César González-Aguilera,Liliana del Rosario Maceo-Gómez,Lic David del Llano Sosa,Raúl Leyva-Castro,Rosa Ojeda-Vázquez. Non-hemodynamic factors associated to the risk of developing hypertensive cardiopathy. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001017; 2: 068-084
-
Lipid-induced cardiovascular diseasesSumeet Manandhar,Sujin Ju,Dong-Hyun Choi,Heesang Song*. Lipid-induced cardiovascular diseases. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001018; 2: 085-094
-
Design and validation of an Index to predict the development of Hypertensive CardiopathyAlexis Álvarez-Aliaga*,Andrés José Quesada-Vázquez,Alexis Suárez-Quesada,David de Llano Sosa. Design and validation of an Index to predict the development of Hypertensive Cardiopathy. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001022; 3: 008-022
-
Endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptors (ESBAR) and its analogs (review)Victor Tsirkin*,Alexander Nozdrachev,Elena Sizova,Tatyana Polezhaeva,Svetlana Khlybova,Marina Morozova,Andrew Trukhin,Julia Korotaeva,Grigory Khodyrev. Endogenous sensitizer of beta-adrenergic receptors (ESBAR) and its analogs (review). . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001028; 3: 064-078
-
Diagnostic accuracy of TIMI versus GRACE score for prediction of death in patients presenting with Acute Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI)Syed Haseeb Raza Naqvi,Tariq Abbas,Han Naung Tun*,Ali Ahmad Naqvi,Zubair Zaffar,Badar ul Ahad Gill,Nisar Ahmad. Diagnostic accuracy of TIMI versus GRACE score for prediction of death in patients presenting with Acute Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI). . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001032; 4: 001-005
-
Cardiomyopathies - The special entity of myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathyFelicitas Escher*,Uwe Kühl,Dirk Lassner,Heinz-Peter Schultheiss. Cardiomyopathies - The special entity of myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001041; 4: 053-070
-
Plaque morphology in diabetic vs. non diabetic patients assessed by Multi-Slice Computed Tomography coronary angiographyHesham Mohamed Aboul-Enein,Amr Elsayed El Naggar,Shereen Ibrahim Farag,Waleed Atef Ahmed Hassan*. Plaque morphology in diabetic vs. non diabetic patients assessed by Multi-Slice Computed Tomography coronary angiography. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001057; 4: 150-155
-
Only low intensity of aerobic exercise improves respiratory compliance in pulmonary hypertensive ratsKatya Rigatto*,Denielli Da SG Bós,Renata Fernandes,Rodrigo B Jaenisch,Pedro Dal Lago. Only low intensity of aerobic exercise improves respiratory compliance in pulmonary hypertensive rats. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001069; 4: 205-209
Recently Viewed
-
Recurrent Pancreatitis Associated with CFTR Heterozygous MutationTuğçe Şevval Yıldız*,Şeyma Şenocak. Recurrent Pancreatitis Associated with CFTR Heterozygous Mutation. Arch Case Rep. 2025: doi: ; 9: 008-011
-
Medical mystery: Deposition of calcium oxalate and phosphate stones in soft tissuesAlessandro Capitanini*,Brunilda Xhaferi,Vincenzo Miniello,Ophelia Meniconi,Claudia Zullo,Claudia Mannucci,Dritan Curi. Medical mystery: Deposition of calcium oxalate and phosphate stones in soft tissues. J Clini Nephrol. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001097; 6: 091-093
-
Inventorization and Exploration of Floral Diversity in Metropolitan Cities of India for Their Suitability in Floriculture of KashmirSheikh Abdul Shakoor*, Shoufar Farooq, Muskan Tareq, Iqra Rashid, Uzmeena Amin, Tehseen Manzoor, Nimra Mukhtar, Tabiya Altaf, Anjum Tehseen, Nazir Ahmad Malla. Inventorization and Exploration of Floral Diversity in Metropolitan Cities of India for Their Suitability in Floriculture of Kashmir. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001144; 8: 121-130
-
Antifungal Efficacy of Panchgavya Formulations against Rhizoctonia solani: An Incitant of Rice Sheath BlightJR Pandya*, JV Patel. Antifungal Efficacy of Panchgavya Formulations against Rhizoctonia solani: An Incitant of Rice Sheath Blight. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001143; 8: 118-120
-
Modulation of Microbiota and its Impact on DepressionKousik Maparu*. Modulation of Microbiota and its Impact on Depression. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001061; 8: 089-090
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."