Abstract
Research Article
Evaluation of the predictive value of CHA2DS2-VASc Score for no-reflow phenomenon in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction who underwent Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Mahmoud Shawky Abd El-Moneum*
Published: 28 October, 2019 | Volume 4 - Issue 3 | Pages: 171-176
Objective: The aim of this study was to estimate the predictive clinical value of CHA2DS2-VASc score for no-reflow phenomena in patients having ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who applied to primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Subjects and Methods: Three-hundred STEMI patients underwent primary PCI. They were classified into: group (1) included 27 patients with no-reflow and group (2) included 273 patients without no-reflow (control). CHA2DS2-VASc risk score was computed for each patient.
Results: This study found statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) in multivariate analysis of the association between CHA2DS2-VASc score and no-reflow phenomenon. The predictive power of individual components in CHA2DS2-VASc score for no-reflow was statistically significant difference (p < 0.05). So, significantly higher CHA2DS2-VASc score is connected with higher risk of no-reflow and in-hospital mortality rate.
Conclusion: Significantly higher CHA2DS2-VASc score is associated with higher risk of no- reflow phenomenon and in-hospital mortality rates in patients with STEMI who underwent primary PCI.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001061 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; Percutaneous coronary intervention; CHA2DS2-VASc score; No-reflow phenomenon
References
- Levine GN, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, Bailey SR, Bittl JA, et al. ACCF/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011; 58: 2550–2583. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22064601
- Jaffe R, Charron T, Puley G, Dick A, Strauss BH. Microvascular obstruction and the no-reflow phenomenon after percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2008; 117: 3152–3156. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18559715
- Durante A, Camici PG. Novel insights into an old phenomenon: the no reflow. Int J Cardiol. 2015; 187: 273–280. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25838230
- Rezkalla SH, Kloner RA. Coronary no-reflow phenomenon: from the experimental laboratory to the cardiac catheterization laboratory. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008; 72: 950–957. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19021281
- Mirbolouk F, Gholipour M, Salari A, Shakiba M, Kheyrkhah J, et al. CHA2DS2-VASc Score Predict No-Reflow Phenomenon in Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2018; 10: 46-52. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29707178
- Ashoori A, Pourhosseini H, Ghodsi S, Salarifar M, Nematipour E, et al. CHA2DS2-VASc Score as an Independent Predictor of Suboptimal Reperfusion and Short-Term Mortality after Primary PCI in Patients with Acute ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019; 55: E35. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30717292
- Bouleti C, Mewton N, Germain S. The no-reflow phenomenon: State of the art. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2015; 108: 661–674. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26616729
- Lip GYH, Nieuwlaat R, Pisters R, Lane DA, Crijns HJ. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: The Euro Heart Survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest. 2010; 137: 263–272. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19762550
- Chan YH, Yiu KH, Lau KK, Lam TH, Lau CP, et al. The CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc scores predict adverse vascular function, ischemic stroke and cardiovascular death in high-risk patients without atrial fibrillation: role of incorporating PR prolongation. Atherosclerosis. 2014; 237: 504–513. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25463082
- O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey DE, Chung MK, et al. 2013 A CCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST–elevation myocardial infarction: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 61: e78. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23247304
- Rasoul S, Dambrink JH, Breeman A, Elvan A, van’t Hof AW. The relation between myocardial blush grade and myocardial contrast echocardiography: Which one is a better predictor of myocardial damage? Neth Heart J. 2010; 18: 25–30. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20111640
- Carrick D, Oldroyd KG, McEntegart M, Haig C, Petrie MC, et al. A randomized trial of deferred stenting versus immediate stenting to prevent No- or slow-reflow in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (DEFER-STEMI). Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63: 2088–2098. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24583294
- Fox KA, Dabbous OH, Goldberg RJ, Pieper KS, Eagle KA, et al. Prediction of risk of death and myocardial infarction in the six months after presentation with acute coronary syndrome: Prospective multinational observational study (GRACE). BMJ. 2006; 333: 1091. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17032691
- Bayramoğlu A, Taşolar H, Kaya A, Tanboğa İH, Yaman M, et al. Prediction of no-reflow and major adverse cardiovascular events with a new scoring system in STEMI patients. J Interv Cardiol. 2018; 31: 144-149. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29193382
- Magro M, Nauta ST, Simsek C, Boersma E, van der Heide E, et al. Usefulness of the SYNTAX Score to Predict “No Reflow” in patients treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2012; 109: 601–606. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22177003
- Ipek G, Onuk T, Karatas MB, Gungor B, Osken A, et al. CHA2DS2-VASc Score is a Predictor of No-Reflow in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Who Underwent Primary Percutaneous Intervention. Angiology. 2015; 67: 840–845. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26685178
- Bozbay M, Uyarel H, Cicek G, Oz A, Keskin M, et al. CHA2DS2-VASc Score Predicts In-Hospital and Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Who Were Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2016; 23: 132–138. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27170782
- Hioki H, Miura T, Miyashita Y, Motoki H, Shimada K, et al. Risk stratification using the CHA2DS2-VASc score in patients with coronary heart disease undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention; sub-analysis of SHINANO registry. IJC Heart Vasc. 2015; 7: 76–81. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28785649
- Ndrepepa G, Tiroch K, Fusaro M, Keta D, Seyfarth M, et al. 5-year prognostic value of no-reflow phenomenon after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 55: 2383–2389. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20488311
- Harrison RW, Aggarwal A, Ou F, Klein LW, Rumsfeld JS, et al. Incidence and outcomes of no-reflow phenomenon during percutaneous coronary intervention among patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2012; 111: 178–184. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23111142
- Nallamothu BK, Bradley EH, Krumholz HM. Time to treatment in primary percutaneous coronary intervention. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357: 1631–1638. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17942875
- Iwakura K, Ito H, Ikushima M, Kawano S, Okamura A, et al. Association between hyperglycemia and the no-reflow phenomenon in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003; 41: 1–7. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12570936
- Dean J, Dela Cruz S, Mehta PK, Merz CNB. Coronary microvascular dysfunction: sex-specific risk, diagnosis, and therapy. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015; 12: 406–414. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26011377
- Kim J, Cha MJ, Lee DH, Lee HS, Nam CM, et al. The association between cerebral atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness in acute ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis. 2011; 219: 887–891. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21974846
- Heusch G. Cardioprotection: Chances and challenges of its translation to the clinic. Lancet. 2013; 381: 166–175. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23095318
- Rezkalla SH, Stankowski RV, Hanna J, Kloner RA. Management of No-Reflow Phenomenon in the catheterization laboratory. J Am Coll Cardiolvasc Interv. 2017; 10: 215–223. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28183461
- De Vita M, Burzotta F, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Lefevre T, Dudek D, et al. Individual patient-date meta-analysis comparing clinical outcome in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction treated with percutaneous Coronary intervention with or without prior thrombectomy. ATTEMPT study: A pooled Analysis of Trials on Thrombectomy in Acute Myocardial infarction based on individual Patient data. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009; 5: 243–247. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19436647
- Chua SK, Lo HM, Chiu CZ, Shyu KG. Use of CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc Scores to Predict Subsequent Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, and Death in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: Data from Taiwan Acute Coronary Syndrome Full Spectrum Registry. PLoS ONE. 2014; 9: e111167. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25343586
- Al-Thani HA, El-Menyar A, Zubaid M, Rashed WA, Ridha M, et al. Peripheral arterial disease in patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome in six middle eastern countries. Int J Vasc Med. 2011; 2011: 815-902. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22220279
Figures:
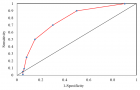
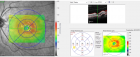
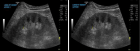
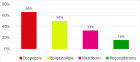
Figure 1
Similar Articles
-
Thrombolysis, the only Optimally Rapid Reperfusion TreatmentVictor Gurewich*. Thrombolysis, the only Optimally Rapid Reperfusion Treatment. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001010; 2: 029-034
-
Incidence of symptom-driven Coronary Angiographic procedures post-drug-eluting Balloon treatment of Coronary Artery drug-eluting stent in-stent Restenosis-does it matter?Victor Voon*,Dikshaini Gumani,Calvin Craig,Ciara Cahill,Khalid Mustafa,Terry Hennessy,Samer Arnous,Thomas Kiernan. Incidence of symptom-driven Coronary Angiographic procedures post-drug-eluting Balloon treatment of Coronary Artery drug-eluting stent in-stent Restenosis-does it matter?. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001011; 2: 035-041
-
Is secondary prevention information before discharge adequate after percutaneous coronary intervention?Catrin Henriksson*,Joep Perk. Is secondary prevention information before discharge adequate after percutaneous coronary intervention?. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001034; 4: 012-020
-
Single-centre real world experience of the Mynx Femoral closure device in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventionThirunavukarasu S,Zaman M,Hayat A,Aghamohammadzadeh R,Malik N*. Single-centre real world experience of the Mynx Femoral closure device in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001036; 4: 030-035
-
Evaluation of the predictive value of CHA2DS2-VASc Score for no-reflow phenomenon in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction who underwent Primary Percutaneous Coronary InterventionMahmoud Shawky Abd El-Moneum*. Evaluation of the predictive value of CHA2DS2-VASc Score for no-reflow phenomenon in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction who underwent Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001061; 4: 171-176
-
Dapt ReviewKARACA Özkan*,KARASU Mehdi,KOBAT Mehmet A,KIVRAK Tarık. Dapt Review. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001088; 5: 060-066
-
Incidence and outcome of no flow after primary percutaneous coronary intervention in acute myocardial infarctionGoutam Datta*. Incidence and outcome of no flow after primary percutaneous coronary intervention in acute myocardial infarction. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001102; 5: 153-156
-
pVAD-assisted left main DK-Crush Bifurcation PCI Post-ViV TAVRSteve Attanasio*,Maria Isabel Camara Planek,Anshuman Das. pVAD-assisted left main DK-Crush Bifurcation PCI Post-ViV TAVR. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001114; 6: 029-032
-
Percutaneous treatment of severe retroperitoneal hematoma after percutaneous coronary interventionAgarwal Rajendra Kumar*,Agarwal Rajiv. Percutaneous treatment of severe retroperitoneal hematoma after percutaneous coronary intervention. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001119; 6: 055-058
-
RV Function by cardiac magnetic resonance and its relationship to RV longitudinal strain and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute inferior ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous interventionSalma Taha*,Shrouk Kelany Ali,Fabrizio D’Ascenzo,Hosam Hasan-Ali,Yousra Ghzally#,Mohamed Abdel Ghany. RV Function by cardiac magnetic resonance and its relationship to RV longitudinal strain and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute inferior ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous intervention. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001120; 6: 059-065
Recently Viewed
-
Trends in TeledentistryRudrakshi C*. Trends in Teledentistry. J Clin Adv Dent. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcad.1001014; 4: 004-005
-
Au26-35: A Special Geometrical Structure of Au33 (D2) Cluster with Highly Occupied - 14 Pairs of Double-State DegeneracyK Vishwanathan*. Au26-35: A Special Geometrical Structure of Au33 (D2) Cluster with Highly Occupied - 14 Pairs of Double-State Degeneracy. Ann Adv Chem. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.aac.1001035; 6: 063-080
-
Texture of Thin Films of Aluminum Nitride Produced by Magnetron SputteringStrunin Vladimir Ivanovich,Baranova Larisa Vasilievna*,Baisova Bibigul Tulegenovna. Texture of Thin Films of Aluminum Nitride Produced by Magnetron Sputtering. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001106; 8: 013-016
-
Minimising Carbon Footprint in Anaesthesia PracticeNisha Gandhi and Abinav Sarvesh SPS*. Minimising Carbon Footprint in Anaesthesia Practice. Int J Clin Anesth Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcar.1001025; 8: 005-007
-
On Friedman equation, quadratic laws and the geometry of our universeS Kalimuthu*. On Friedman equation, quadratic laws and the geometry of our universe. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001041; 4: 048-050
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."